Concepts Used
DFS , Recursion, Stack
Difficulty Level
Easy
Problem Statement :
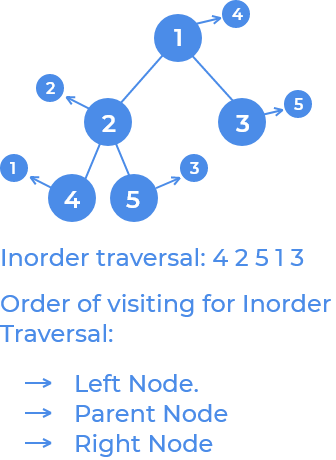
Given a binary tree, our task is to print the inorder traversal of the tree.
Solution Approach :
Introduction :
In this traversal the left subtree is visited first, then the root followed by the right sub-tree.
Method 1 (Using Stack) :
We will use the Stack to store the traversal, we need to traverse the left node, then root, followed by the right node.
We will create an empty stack S, and perform following steps :
- Start from the root, call it current .
- If current is not NULL, push current on to
S. - Move to left child of current and go to step 2.
- If current == NULL and !stack.empty(), current = s.pop.
- Process current and set current = current.right, go to step
- Stop once current becomes NULL.
Below is the implementation of this aproach (see C++ Implementation).
Method 2 (Using Recursion) :
We can also print the Inorder traversal of a binary tree with root R using recursion.
-
The idea is to visit the left subtree by recursively calling,
func(R->left). -
Then, visit the root node & print its value,
func(R->value). -
At last, we will visit right subtree by recursively calling,
func(R->right).
Complexity Analysis :
Time complexity of method 1 is
O(n), wherenis the number of nodes. Since we are visiting each nodes once.Space complexity is
O(n)as well, because of the stack which is storing atmostnnodes.
SOLUTIONS:
#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define ll long long
#define REP(i, n) for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
struct nodelist
{
ll value;
struct nodelist *left;
struct nodelist *right;
};
typedef struct nodelist node;
struct Queue
{
int front, rear, size;
unsigned capacity;
node* *array;
};
typedef struct Queue queue;
queue* createQueue(unsigned capacity)
{
queue* qu =(queue*)malloc(sizeof(queue));
qu->capacity = capacity;
qu->front = qu->size =0;
qu->rear = capacity-1;
qu->array = (node **)malloc(qu->capacity * sizeof(node));
return qu;
}
int isFull(queue* queue1)
{
return (queue1->size == queue1->capacity);
}
int isEmpty(queue* queue1)
{
return (queue1->size==0);
}
void enqueue(queue* queue1, node* item)
{
if(isFull(queue1))
return ;
queue1->rear = (queue1->rear +1 )%queue1->capacity;
queue1->array[queue1->rear] = item;
queue1->size = queue1->size +1;
}
node dequeue(queue* queue1)
{
node* item = queue1->array[queue1->front];
queue1->front = (queue1->front +1)%queue1->capacity;
queue1->size = queue1->size -1;
return *item;
}
node* front(queue* queue1)
{
return queue1->array[queue1->front];
}
node* rear(queue * queue1)
{
return queue1->array[queue1->rear];
}
node *createNode(ll value)
{
node *t= (node *) malloc(sizeof(node));
t->value = value;
t->right = t->left = NULL;
return t;
}
void deleteNode(node*t)
{
free(t);
}
node *replaceNegativeOne(node *root)
{
if(root==NULL ||(root->value == -1 && root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL))
return NULL;
root->left = replaceNegativeOne(root->left);
root->right = replaceNegativeOne(root->right);
return root;
}
void deleteTree(node *node1)
{
if(node1==NULL)
return;
deleteTree(node1->left);
deleteTree(node1->right);
free(node1);
}
node *createTreeByLevelTree()
{
ll n,m;
queue* queue1 = createQueue(100000);
node *root, *t;
root = NULL;
while(scanf("%lld", &n))
{
if(isEmpty(queue1))
{
root= createNode(n);
enqueue(queue1,root);
continue;
}
scanf("%lld", &m);
t = front(queue1);
dequeue(queue1);
t->left =createNode(n);
t->right=createNode(m);
if(t->left->value !=-1)
enqueue(queue1,t->left);
if(t->right->value !=-1)
enqueue(queue1,t->right);
if(isEmpty(queue1))
break;
}
return root;
}
void inOrderTraversal(node *t)
{
if(t==NULL)
return;
inOrderTraversal(t->left);
printf("%d ",t->value);
inOrderTraversal(t->right);
}
int main() {
node *root = NULL;
root = createTreeByLevelTree();
root = replaceNegativeOne(root);
inOrderTraversal(root);
deleteTree(root);
return 0;
}
#define REP(i, n) for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
#define pb(a) push_back(a)
#define vi vector<long>
#define ll long long
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
ll value;
node *left;
node *right;
};
node *createNode(ll value)
{
node *t = new node();
t->value = value;
t->right = t->left = NULL;
return t;
}
void deleteNode(node *t)
{
delete t;
}
node *replaceNegativeOne(node *root)
{
if (root == NULL || (root->value == -1 && root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL))
return NULL;
root->left = replaceNegativeOne(root->left);
root->right = replaceNegativeOne(root->right);
return root;
}
node *createTreeByLevelTree()
{
ll n, m;
queue<node *> q;
node *root, *t;
root = NULL;
while (cin >> n)
{
if (q.empty())
{
root = createNode(n);
q.push(root);
continue;
}
cin >> m;
t = q.front();
q.pop();
t->left = createNode(n);
t->right = createNode(m);
if (t->left->value != -1)
{
q.push(t->left);
}
if (t->right->value != -1)
{
q.push(t->right);
}
}
return root;
}
void deleteTree(node *node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
deleteTree(node->left);
deleteTree(node->right);
delete node;
}
void inOrderTraversal(node *t)
{
stack<node *> s;
node *curr = t;
while (curr != NULL || s.empty() == false)
{
while (curr != NULL)
{
s.push(curr);
curr = curr->left;
}
curr = s.top();
s.pop();
cout << curr->value << " ";
curr = curr->right;
}
}
int main()
{
node *root = NULL;
root = createTreeByLevelTree();
root = replaceNegativeOne(root);
inOrderTraversal(root);
//doYourThing(root);
deleteTree(root);
return 0;
}
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.io.*;
class Node
{
long value;
Node left, right;
public Node(long item)
{
value = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree {
Node root;
BinaryTree() {
root = null;
}
Node createNode(long value) {
Node t = new Node(value);
return t;
}
Node replaceNegativeOne(Node root) {
if (root == null || (root.value == -1 && root.left == null && root.right == null)) {
return null;
}
root.left = replaceNegativeOne(root.left);
root.right = replaceNegativeOne(root.right);
return root;
}
Node createTreeByLevelTree() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
long n, m;
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Node t;
root = null;
while (sc.hasNext()) {
n = sc.nextLong();
if (queue.isEmpty()) {
root = createNode(n);
((LinkedList<Node>) queue).add(root);
continue;
}
m = sc.nextLong();
t = ((LinkedList<Node>) queue).peekFirst();
((LinkedList<Node>) queue).pop();
t.left = createNode(n);
t.right = createNode(m);
if (t.left.value != -1)
((LinkedList<Node>) queue).add(t.left);
if (t.right.value != -1)
((LinkedList<Node>) queue).add(t.right);
if (queue.isEmpty())
break;
}
return root;
}
void deleteTree(Node node) {
node = null;
}
void inOrderTraversal(Node node) {
if(node==null)
return;
inOrderTraversal(node.left);
System.out.print(node.value+" ");
inOrderTraversal(node.right);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// write your code here
BinaryTree bt = new BinaryTree();
bt.root = bt.createTreeByLevelTree();
bt.root = bt.replaceNegativeOne(bt.root);
bt.inOrderTraversal(bt.root);
bt.deleteTree(bt.root);
}
}
[forminator_quiz id="1696"]
This article tried to discuss DFS , Recursion, Stack. Hope this blog helps you understand and solve the problem. To practice more problems on DFS , Recursion, Stack you can check out .