Concepts Used
BFS , Recursion
Difficulty Level
Easy
Problem Statement :
Given a binary tree, our task is to print the size of the tree. Size of tree represented as the number of nodes in the given tree.
Solution Approach :
Introduction :
The size of the tree is the total count of the nodes present in the tree. Total nodes present is the sum of the count of nodes present in left & right subtree plus 1 (root node).
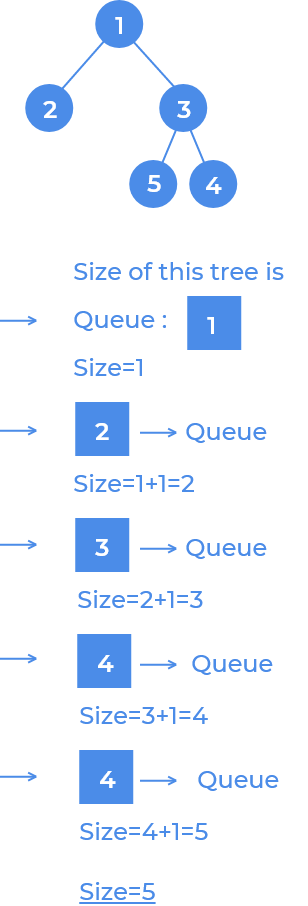
Method 1(using Queue):
We can use a queue to perform level order traversal. We will perform following operations :
- Create an empty queue q and a counter to store the size.
- push the root node into the queue
(q.push(root))and do following whileqis not empty:
- pop the front element of queue (
temp=q.front()).- if
temp->left&temp->rightis not NULL, push them into theq.- Increment the counter every time we push a node, by
1.- Return counter.
Method 2 (Recursion) :
Introduction says it all, all we need is to store the count of left subtree & right subree recursively.
Now we will increment our sum by 1 to count the root node.
We will do the same for left & right subtrees by recursively calling , root->left & root->right.
Solutions:
#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define ll long long
#define REP(i, n) for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
struct nodelist
{
ll value;
struct nodelist *left;
struct nodelist *right;
};
typedef struct nodelist node;
struct Queue
{
int front, rear, size;
unsigned capacity;
node* *array;
};
typedef struct Queue queue;
queue* createQueue(unsigned capacity)
{
queue* qu =(queue*)malloc(sizeof(queue));
qu->capacity = capacity;
qu->front = qu->size =0;
qu->rear = capacity-1;
qu->array = (node **)malloc(qu->capacity * sizeof(node));
return qu;
}
int isFull(queue* queue1)
{
return (queue1->size == queue1->capacity);
}
int isEmpty(queue* queue1)
{
return (queue1->size==0);
}
void enqueue(queue* queue1, node* item)
{
if(isFull(queue1))
return ;
queue1->rear = (queue1->rear +1 )%queue1->capacity;
queue1->array[queue1->rear] = item;
queue1->size = queue1->size +1;
}
node dequeue(queue* queue1)
{
node* item = queue1->array[queue1->front];
queue1->front = (queue1->front +1)%queue1->capacity;
queue1->size = queue1->size -1;
return *item;
}
node* front(queue* queue1)
{
return queue1->array[queue1->front];
}
node* rear(queue * queue1)
{
return queue1->array[queue1->rear];
}
node *createNode(ll value)
{
node *t= (node *) malloc(sizeof(node));
t->value = value;
t->right = t->left = NULL;
return t;
}
void deleteNode(node*t)
{
free(t);
}
node *replaceNegativeOne(node *root)
{
if(root==NULL ||(root->value == -1 && root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL))
return NULL;
root->left = replaceNegativeOne(root->left);
root->right = replaceNegativeOne(root->right);
return root;
}
void deleteTree(node *node1)
{
if(node1==NULL)
return;
deleteTree(node1->left);
deleteTree(node1->right);
free(node1);
}
node *createTreeByLevelTree()
{
ll n,m;
queue* queue1 = createQueue(100000);
node *root, *t;
root = NULL;
while(scanf("%lld", &n))
{
if(isEmpty(queue1))
{
root= createNode(n);
enqueue(queue1,root);
continue;
}
scanf("%lld", &m);
t = front(queue1);
dequeue(queue1);
t->left =createNode(n);
t->right=createNode(m);
if(t->left->value !=-1)
enqueue(queue1,t->left);
if(t->right->value !=-1)
enqueue(queue1,t->right);
if(isEmpty(queue1))
break;
}
return root;
}
int calculateSize(node *t)
{
if(t == NULL)
return 0;
return 1+calculateSize(t->left) + calculateSize(t->right);
}
int main() {
node *root = NULL;
root = createTreeByLevelTree();
root = replaceNegativeOne(root);
printf("%d ",calculateSize(root));
deleteTree(root);
return 0;
}
#define REP(i, n) for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
#define pb(a) push_back(a)
#define vi vector<long>
#define ll long long
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
ll value;
node *left;
node *right;
};
node *createNode(ll value)
{
node *t = new node();
t->value = value;
t->right = t->left = NULL;
return t;
}
void deleteNode(node *t)
{
delete t;
}
node *replaceNegativeOne(node *root)
{
if (root == NULL || (root->value == -1 && root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL))
return NULL;
root->left = replaceNegativeOne(root->left);
root->right = replaceNegativeOne(root->right);
return root;
}
node *createTreeByLevelTree()
{
ll n, m;
queue<node *> q;
node *root, *t;
root = NULL;
while (cin >> n)
{
if (q.empty())
{
root = createNode(n);
q.push(root);
continue;
}
cin >> m;
t = q.front();
q.pop();
t->left = createNode(n);
t->right = createNode(m);
if (t->left->value != -1)
{
q.push(t->left);
}
if (t->right->value != -1)
{
q.push(t->right);
}
}
return root;
}
void deleteTree(node *node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
deleteTree(node->left);
deleteTree(node->right);
delete node;
}
int calculateSize(node* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
return 0;
queue<node *> q;
int count = 1;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
node *temp = q.front();
if(temp->left)
{
q.push(temp->left);
count++;
}
if(temp->right)
{
q.push(temp->right);
count++;
}
q.pop();
}
return count;
}
int main()
{
node *root = NULL;
root = createTreeByLevelTree();
root = replaceNegativeOne(root);
cout<< calculateSize(root)<<endl;
deleteTree(root);
return 0;
}
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.io.*;
class Node
{
long value;
Node left, right;
public Node(long item)
{
value = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree {
Node root;
BinaryTree() {
root = null;
}
Node createNode(long value) {
Node t = new Node(value);
return t;
}
Node replaceNegativeOne(Node root) {
if (root == null || (root.value == -1 && root.left == null && root.right == null)) {
return null;
}
root.left = replaceNegativeOne(root.left);
root.right = replaceNegativeOne(root.right);
return root;
}
Node createTreeByLevelTree() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
long n, m;
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Node t;
root = null;
while (sc.hasNext()) {
n = sc.nextLong();
if (queue.isEmpty()) {
root = createNode(n);
((LinkedList<Node>) queue).add(root);
continue;
}
m = sc.nextLong();
t = ((LinkedList<Node>) queue).peekFirst();
((LinkedList<Node>) queue).pop();
t.left = createNode(n);
t.right = createNode(m);
if (t.left.value != -1)
((LinkedList<Node>) queue).add(t.left);
if (t.right.value != -1)
((LinkedList<Node>) queue).add(t.right);
if (queue.isEmpty())
break;
}
return root;
}
void deleteTree(Node node) {
node = null;
}
int calculateSize(Node node) {
if(node == null)
return 0;
return 1+calculateSize(node.left)+calculateSize(node.right);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// write your code here
BinaryTree bt = new BinaryTree();
bt.root = bt.createTreeByLevelTree();
bt.root = bt.replaceNegativeOne(bt.root);
System.out.println(bt.calculateSize(bt.root));
bt.deleteTree(bt.root);
}
}
[forminator_quiz id="1772"]
This article tried to discuss BFS , Recursion. Hope this blog helps you understand and solve the problem. To practice more problems on BFS , Recursion you can check out .