Concepts Used:
Sorting
Difficulty Level:
Easy
Problem Statement (Simplified):
We have to print the array containing
0s,1s and2s in non-decreasing order.
Test Case:
Input:
1
10
0 1 0 0 1 0 2 2 0 1
Output:
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 2 2
Explanation:
We can get this answer after sorting the whole array.Solving Approach :
1) Here we can sort the array too but that would cost us at least
O(N x log(n))if we use Merge Sort.2) We know array contains only three elements i.e.
0s, 1s and2s, we can count their total number of occurrences in the array.3) We later can print
0s, 1s and2s number of times they appear in array.4) For example if
0appearsatimes,1appearsbtimes,and2appearsctimes, then we’ll print0foratimes first then1forbtimes and print2forctimes aferwards.
Approach-1 : Using Sorting (Merge Sort)
We can sort array and print it, it takes O(
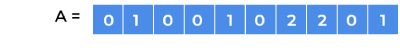
N x log(N))Let, array
Abe,
Sorting array
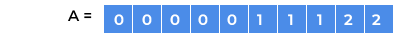
Aproduces our answer that is,
Approach-2 : Using counters
We know, array contains only 0, 1, and 2 as elements, so we find total number of appearances of 0,1, and 2 and print them in order. This take O(
N) time complexity.Let, the array
Abe,
We maintain hash table
Hfor counting 0, 1, and 2, hash table after counting is,
So our final answer is,
Solutions:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int test;
scanf("%d",&test);
while(test--){
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
int arr[n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
int count[3] = {0};
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
count[arr[i]]++;
for(int i=0; i<=2;i++)
for(int j=0; j<count[i]; j++)
printf("%d ",i);
printf("\n");
}
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int test;
cin>>test;
while(test--){
int n;
cin>>n;
int arr[n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
cin>>arr[i];
int count[3] = {0};
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
count[arr[i]]++;
for(int i=0; i<=2;i++)
for(int j=0; j<count[i]; j++)
cout<<i<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
}
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int test = sc.nextInt();
while(test--!=0){
int n = sc.nextInt();
int arr[] = new int[n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
int count[] = new int[3];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
count[arr[i]]++;
for(int i=0; i<=2;i++)
for(int j=0; j<count[i]; j++)
System.out.print(i+" ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
for _ in range(int(input())): n = int(input()) arr = list(map(int,input().split())) count = [0] * 3 for i in arr: count[i] += 1 for i in range(3): for j in range(count[i]): print(i, end = " ") print()
[forminator_quiz id="1136"]
This article tried to discuss the concept of sorting. Hope this blog helps you understand and solve the problem. To practice more problems on sorting you can check out .