CONCEPTS USED:
Recursion
DIFFICULTY LEVEL:
Easy
PROBLEM STATEMENT(SIMPLIFIED):
Given a number N, print its decreasing sequence (i.e. keep subtracting by 5) till it reaches (<=0) and then print its increasing sequence(i.e. keep adding by 5) till it reaches N again.
For Example:
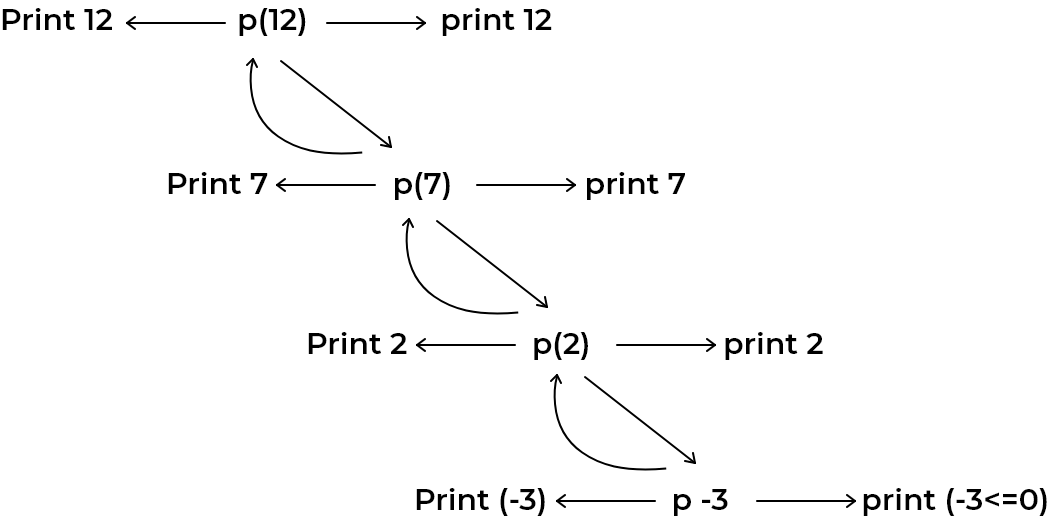
Input : 12
Output : 12 7 2 -3 2 7 12SOLVING APPROACH:
Recursively keep printing value of N and decrementing it by 5 until it becomes less than equal to 0.
Then print the same values in reverse fashion using
Tail Recursion.
STATE SPACE TREE:
SOLUTIONS:
#include <stdio.h>
void print_pattern(int n){
if(n <= 0){
printf("%d ",n);
return;
}
printf("%d ",n);
print_pattern(n-5);
printf("%d ",n);
}
int main(){
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
print_pattern(n);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void print_pattern(int n){
if(n <= 0){
cout<<n<<" ";
return;
}
cout<<n<<" ";
print_pattern(n-5);
cout<<n<<" ";
}
int main(){
int t;cin>>t;
while(t--){
int n;cin>>n;
print_pattern(n);
cout<<"\n";
}
return 0;
}
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
static void print_pattern(int n){
if(n <= 0){
System.out.print(n + " ");
return;
}
System.out.print(n + " ");
print_pattern(n-5);
System.out.print(n + " ");
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int t = sc.nextInt();
while(t!=0){
int n = sc.nextInt();
print_pattern(n);
System.out.println();
t--;
}
}
}
def print_pattern(n): if n <= 0: print(n, end = " ") return print(n, end = " ") print_pattern(n - 5) print(n, end = " ") for _ in range(int(input())): n = int(input()) print_pattern(n) print()
[forminator_quiz id="968"]
This article tried to discuss Recursion. Hope this blog helps you understand and solve the problem. To practice more problems on Recursion you can check out .