CONCEPTS USED:
Recursion
DIFFICULTY LEVEL:
Easy
PROBLEM STATEMENT(SIMPLIFIED):
Given a number N, your task is to print all even numbers (>0) from 1 to N using recursion.
For Example:
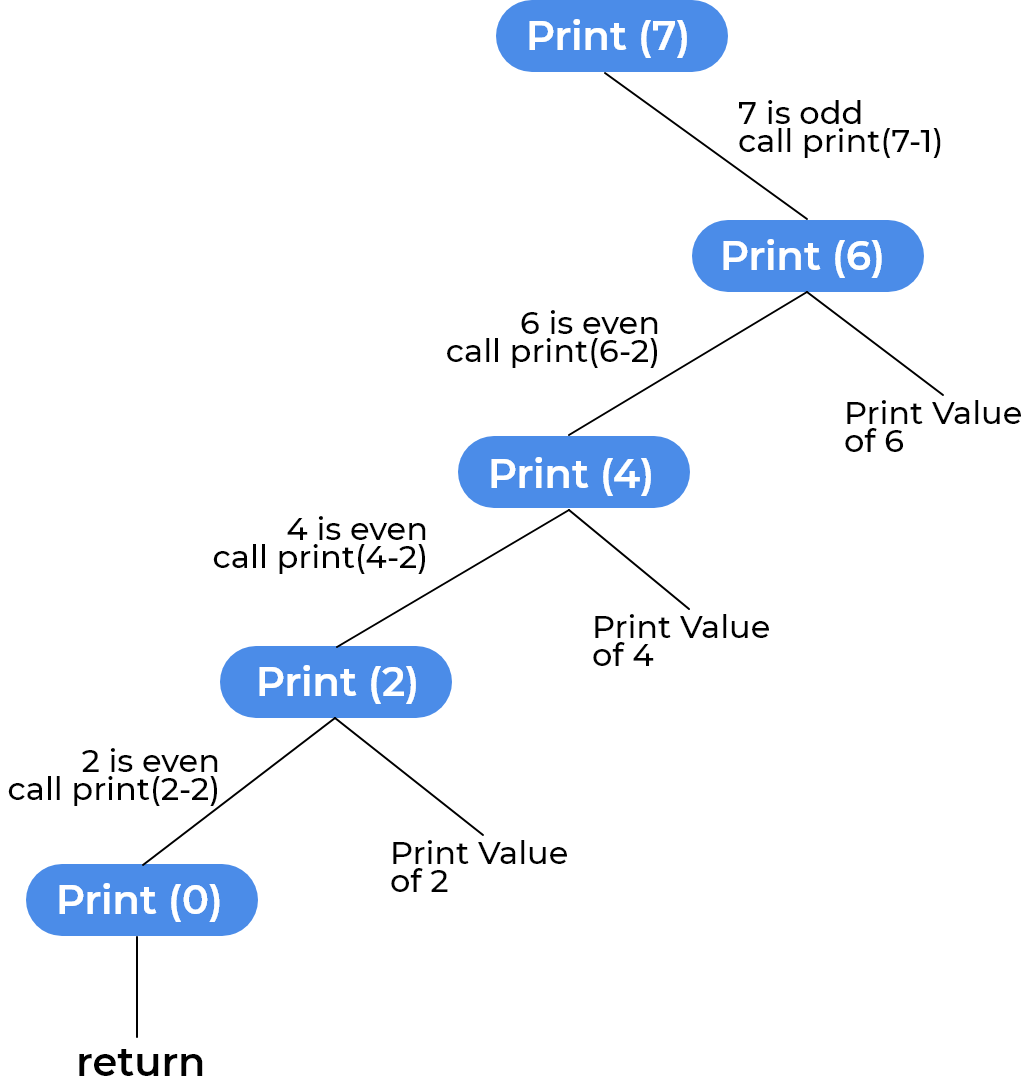
Input : N = 7
Output : 2 4 6SOLVING APPROACH:
- Check if the value of N is even, recursively go on checking for other values of N-2 and print this value.
- If the value of N is odd, recursively go on checking for (N-1) as (N-1) would be even.
- If at any point, N becomes (<=0), simply return.
ALGORITHM:
if (n <= 0)
exit
if (n is even)
check for (n-2) and print n
if (n is odd)
check for (n-1)STATE SPACE TREE:
SOLUTIONS:
#include <stdio.h>
void printEven(int n){
if(n <= 0) //if n becomes less than equal to 0
return ;
if( n%2 == 0){
printEven(n-2); //if n is even go for smaller values of n and finally print all
printf("%d ",n);
}
else
printEven(n-1); //if n is odd recurse for n-1 values as it will be even
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
printEven(n);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void printEven(int n){
if(n <= 0) //if n becomes less than equal to 0
return ;
if( n%2 == 0){
printEven(n-2); //if n is even go for smaller values of n and finally print all
cout<<n<<" ";
}
else
printEven(n-1); //if n is odd recurse for n-1 values as it will be even
}
int main()
{
int t;cin>>t;
while(t--){
int n;cin>>n;
printEven(n);
cout<<"\n";
}
return 0;
}
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int t = sc.nextInt();
while(t!=0)
{
int arr_x[] = new int[4];
int arr_y[] = new int[4];
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
arr_x[i] = sc.nextInt();
arr_y[i] = sc.nextInt();;
}
int dist_12 = (arr_x[0]-arr_x[1])*(arr_x[0]-arr_x[1]) + (arr_y[0]-arr_y[1])*(arr_y[0]-arr_y[1]);
int dist_34 = (arr_x[2]-arr_x[3])*(arr_x[2]-arr_x[3]) + (arr_y[2]-arr_y[3])*(arr_y[2]-arr_y[3]);
int midx_12 = (arr_x[0]+arr_x[1])/2;
int midy_12 = (arr_y[0]+arr_y[1])/2;
int midx_34 = (arr_x[2]+arr_x[3])/2;
int midy_34 = (arr_y[2]+arr_y[3])/2;
if(dist_12 == dist_34 && midx_12==midx_34 && midy_12==midy_34)
{
System.out.println("Yes");
}
else
{
System.out.println("No");
}
t--;
}
}
}
def printEven(n): if(n <= 0): return if( n%2 == 0): printEven(n - 2) print(n, end = " ") else: printEven(n - 1) for _ in range(int(input())): n = int(input()) printEven(n) print()
[forminator_quiz id="1007"]
This article tried to discuss the concept of Recursion. Hope this blog helps you understand and solve the problem. To practice more problems on Recursion you can check out .