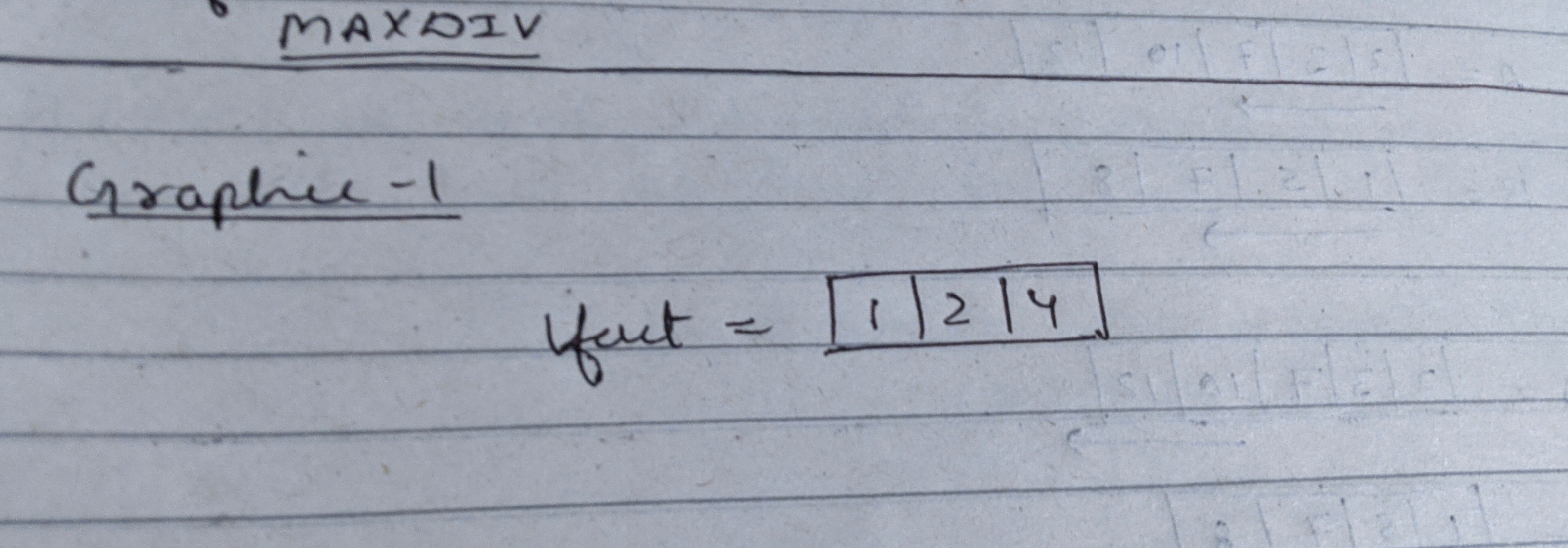Concepts Used
Sorting
Difficulty Level
Hard, Mathematics
Problem Statement (Simplified):
For a given range p and q, find the highest common factor of two given numbers, i.e. a and b. If no such number exists, return -1.
Test Case
Input:
8 12
4
2 10
3 7
2 2
5 6
Output:
4
4
2
-1
Explanation:
For 8 and 12, common divisors are [1,2,4].
In the range [2,10] we have 4 which is the maximum divisor in range.
In the range [3,7] we have 4 which is the maximum divisor in range.
In the range [2,2] we have 2 which is the maximum divisor in range.
In the range [5,6], there lies no divisor so we print -1.Solving Approach :
1) The Highest common factor of any both numbers will be
gcd(a,b)and there exists no factor above this.
2) So, to calculate all the factors we check all number which divideaandbboth from 1 togcd(a,b)and save them in an array.
3) We sort the array containing all common factors so that all factors are organized and searching factors in the range are easier.
4) Highest common factor in the given range [p,q] can be found by searching lower bound ofpand upper bound ofq. Where,
- Upper Bound: Upper bound of any number
Kreturns the position of immediate next number which exists in the array and is just greater thanK.- Lower Bound: Lower bound of any number
Kreturns the position of immediate previous number which exists in the array and is just smaller thanK.
5) If the lower bound ofpand upper bound ofqis the same that means, there is no common factor in the range [p,q].
6) If they are not same, the Highest Common factor in range will be the previous element to element at upper bound ofq, as an element at the upper bound is greater thanq, and element previous to it will be smaller thanqand will be a common factor. Hence it is our answer, so we return the element.
Example
Let given numbers be
a=8andb=12We find
gcd(a,b)as no factor lies beyondgcd(a,b)which divided both numbers, hence,
gcd(a,b)=4We check all numbers between 1 and
gcd(a,b)which divides both of our numbersaandb, we save such numbers in a array,
We also sort this array so that factors are arranged in increasing order,
For given query
pandq, we checklowerboundofpandupperboundofq, let’s assume two queries
- Query-1:
p=5andq=6Here,
lowerBound(p) = 4andupperBound(q)=4, as both values are same that means our query is beyond the range of factors, hence we return -1.
- Query-2:
p=2andq=3Here,
lowerBound(p) = 2andupperBound(q)=4, as both values are not same that means our range coincides with range of factors, hence our answer lies at factor less than upperBound(q) i.e. 3.
Solutions
#include <stdio.h>
int gcd(int a, int b){
while(a!=0 && b!=0){
if(b%a==0)
return a;
int temp = a;
a = b%a;
b = temp;
}
return a;
}
int lowerBound(int a[], int start, int end, int key){
if (start > end)
return end;
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if (a[mid] == key)
return mid;
else if (a[mid] > key)
return lowerBound(a, start, mid-1, key);
else
return lowerBound(a, mid+1, end, key);
}
int upperBound(int a[], int start, int end, int key){
if (start > end)
return start;
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if (a[mid] == key)
return upperBound(a, mid+1, end, key);
else if (a[mid] > key)
return upperBound(a, start, mid-1, key);
else
return upperBound(a, mid+1, end, key);
}
int main()
{
int a,b;
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
int g = (a<b)?gcd(a,b):gcd(b,a);
int divisors[9999999]={0}, count=0;
for(int i=1; i<=g; i++)
if(g%i==0)
divisors[count++] = i;
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
while(n--){
int low,high;
scanf("%d%d",&low,&high);
int id1 = lowerBound(divisors,0,count-1, low);
int id2 = upperBound(divisors,0,count-1, high);
if(low>divisors[id1] || count==0)
id1++;
int diff = id2 - id1;
if(diff == 0)
printf("-1\n");
else
printf("%d\n", divisors[id2-1]);
}
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int gcd(int a, int b){
while(a!=0 && b!=0){
if(b%a==0)
return a;
int temp = a;
a = b%a;
b = temp;
}
return a;
}
int lowerBound(int a[], int start, int end, int key){
if (start > end)
return end;
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if (a[mid] == key)
return mid;
else if (a[mid] > key)
return lowerBound(a, start, mid-1, key);
else
return lowerBound(a, mid+1, end, key);
}
int upperBound(int a[], int start, int end, int key){
if (start > end)
return start;
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if (a[mid] == key)
return upperBound(a, mid+1, end, key);
else if (a[mid] > key)
return upperBound(a, start, mid-1, key);
else
return upperBound(a, mid+1, end, key);
}
int main()
{
int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
int g = (a<b)?gcd(a,b):gcd(b,a);
int divisors[9999999]={0}, count=0;
for(int i=1; i<=g; i++)
if(g%i==0)
divisors[count++] = i;
int n;
cin>>n;
while(n--){
int low,high;
cin>>low>>high;
int id1 = lowerBound(divisors,0,count-1, low);
int id2 = upperBound(divisors,0,count-1, high);
if(low>divisors[id1] || count==0)
id1++;
int diff = id2 - id1;
if(diff == 0)
cout<<"-1\n";
else
cout<<divisors[id2-1]<<endl;
}
}
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
static int gcd(int a, int b){
while(a!=0 && b!=0){
if(b%a==0)
return a;
int temp = a;
a = b%a;
b = temp;
}
return a;
}
static int lowerBound(int a[], int start, int end, int key){
if (start > end)
return end;
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if (a[mid] == key)
return mid;
else if (a[mid] > key)
return lowerBound(a, start, mid-1, key);
else
return lowerBound(a, mid+1, end, key);
}
static int upperBound(int a[], int start, int end, int key){
if (start > end)
return start;
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if (a[mid] == key)
return upperBound(a, mid+1, end, key);
else if (a[mid] > key)
return upperBound(a, start, mid-1, key);
else
return upperBound(a, mid+1, end, key);
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt(),b = sc.nextInt();
int g = (a<b)?gcd(a,b):gcd(b,a);
int divisors[] = new int[9999999], count=0;
for(int i=1; i<=g; i++)
if(g%i==0)
divisors[count++] = i;
int n = sc.nextInt();
while(n--!=0){
int low = sc.nextInt(),high = sc.nextInt();
int id1 = lowerBound(divisors,0,count-1, low);
int id2 = upperBound(divisors,0,count-1, high);
if(count==0 || low>divisors[id1])
id1++;
int diff = id2 - id1;
if(diff == 0)
System.out.println("-1");
else
System.out.println(divisors[id2-1]);
}
}
}
[forminator_quiz id="1237"]
Space Complexity is O(
min(A,B)) to save all common factors.
This article tried to discuss the concept of Sorting. Hope this blog helps you understand the implementation. To practice more problems you can check out .