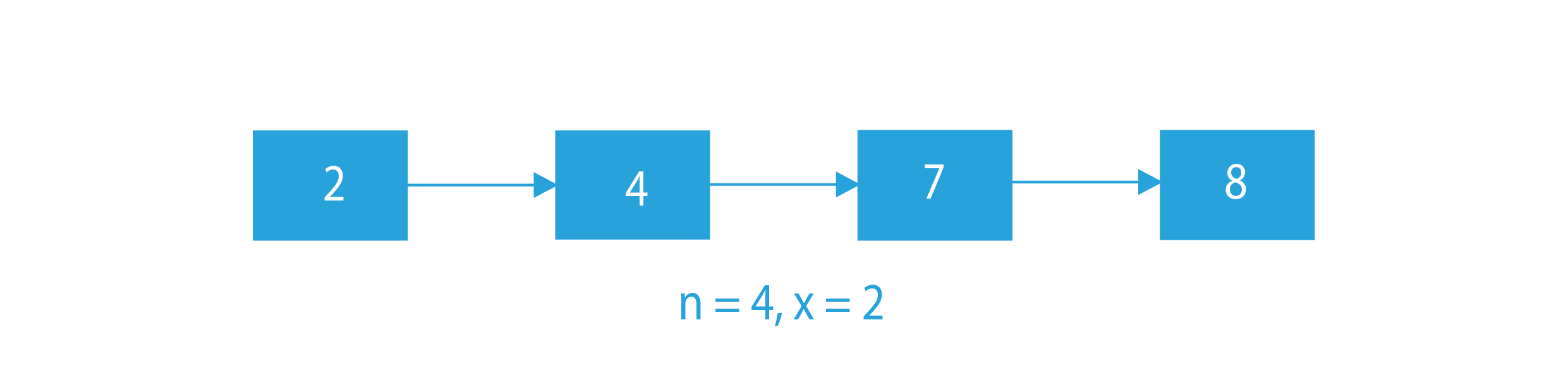Introduction
The linked list is one of the most important concepts and data structures to learn while preparing for interviews. Having a good grasp of Linked Lists can be a huge plus point in a coding interview.
Problem Statement
Insert a node after the n-th node from the end of Linked list.
Problem Statement Understanding
In this problem, we are given a linked list, an integer N and another integer X. We have to traverse till the Nth node from the end and insert X there.
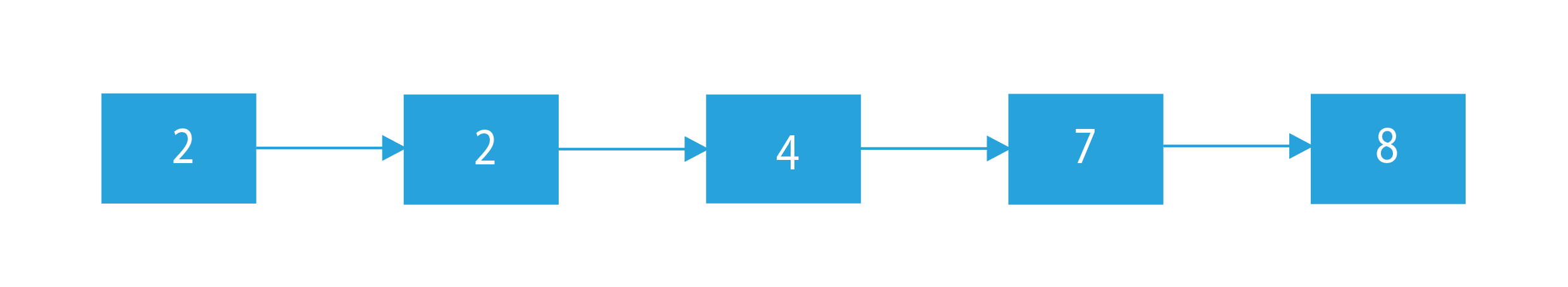
Suppose the linked list is 2 -> 4 -> 7 -> 8, N=4 and X=2. Here, we have to insert 2 after the 4th node from the end. Now, the 4th node from the end is the head node (2). So, we will have to insert the new node after the head node.
The final linked list will be 2 -> 2 -> 4 -> 7 -> 8.
Input:
Output:
Explanation: 4th node from the end is 2 and insertion has been done after this node.
We are going to see two approaches to this problem. One approach will make use of finding the length of the given linked list, and the other approach will use the slow and fast pointer method.
Approach#1
In this approach, we will first find the length of the linked list. Let it be K. Now, we will traverse the list from the 1st node to the (K-N+1)th node from the beginning and insert the given new node after this node. This approach requires two full traversals of the list.
Algorithm
- If the linked list is empty, we will simply terminate the method.
- If the base case fails, then we will proceed further and find the length of the linked list using a while loop.
- If the length of the linked list is K, then traverse from the 1st node to the (K-N+1)th node. After the traversal, insert the given node at that position.
Code Implementation
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
struct Node* getNode(int data)
{
struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
// Function to insert a node at the n-th position from the end
void insertAfterNthNode(struct Node* head, int n, int x)
{
if (head == NULL)
return;
struct Node* newNode = getNode(x);
struct Node* ptr = head;
int len = 0, i;
// Calculation the length of the linked list
while (ptr != NULL) {
len++;
ptr = ptr->next;
}
// Traverse till the n-th node from the end
ptr = head;
for (i = 1; i <= (len - n); i++)
ptr = ptr->next;
// Insert the given node at this position
newNode->next = ptr->next;
ptr->next = newNode;
}
void printList(struct Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
printf("%d ",&head->data);
head = head->next;
}
}
int main()
{
struct Node* head = getNode(2);
head->next = getNode(4);
head->next->next = getNode(7);
head->next->next->next = getNode(8);
int n = 4;
int x = 2;
printf("Original Linked List: ");
printList(head);
insertAfterNthNode(head, n, x);
printf("\nLinked List After Insertion: ");
printList(head);
return 0;
}
#include <bits stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* getNode(int data)
{
Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
// Function to insert a node at the n-th position from the end
void insertAfterNthNode(Node* head, int n, int x)
{
if (head == NULL)
return;
Node* newNode = getNode(x);
Node* ptr = head;
int len = 0, i;
// Calculation the length of the linked list
while (ptr != NULL) {
len++;
ptr = ptr->next;
}
// Traverse till the n-th node from the end
ptr = head;
for (i = 1; i <= (len - n); i++)
ptr = ptr->next;
// Insert the given node at this position
newNode->next = ptr->next;
ptr->next = newNode;
}
void printList(Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
cout << head->data << " ";
head = head->next;
}
}
int main()
{
Node* head = getNode(2);
head->next = getNode(4);
head->next->next = getNode(7);
head->next->next->next = getNode(8);
int n = 4;
int x = 2;
cout << "Original Linked List: ";
printList(head);
insertAfterNthNode(head, n, x);
cout << "\nLinked List After Insertion: ";
printList(head);
return 0;
}
public class PrepBytes
{
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
}
static Node getNode(int data)
{
Node newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = data;
newNode.next = null;
return newNode;
}
static void insertAfterNthNode(Node head, int n, int x)
{
if (head == null)
return;
Node newNode = getNode(x);
Node ptr = head;
int len = 0, i;
while (ptr != null)
{
len++;
ptr = ptr.next;
}
ptr = head;
for (i = 1; i <= (len - n); i++)
ptr = ptr.next;
newNode.next = ptr.next;
ptr.next = newNode;
}
static void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null)
{
System.out.print(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node head = getNode(2);
head.next = getNode(4);
head.next.next = getNode(7);
head.next.next.next = getNode(8);
int n = 4, x = 2;
System.out.print("Original Linked List: ");
printList(head);
insertAfterNthNode(head, n, x);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("Linked List After Insertion: ");
printList(head);
}
}
# A linked list Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.nextNode = None
# function to create and return a Node
def getNode(data):
newNode = Node(data)
return newNode
# function to insert a Node at required position
def insertPos(headNode, position, data):
head = headNode
if (position < 1):
print("Invalid position!")
if position == 1:
newNode = Node(data)
newNode.nextNode = headNode
head = newNode
else:
while (position != 0):
position -= 1
if (position == 1):
newNode = getNode(data)
newNode.nextNode = headNode.nextNode
headNode.nextNode = newNode
break
headNode = headNode.nextNode
if headNode == None:
break
if position != 1:
print("position out of range")
return head
def printList(head):
while (head != None):
print(' ' + str(head.data), end = '')
head = head.nextNode
print()
if __name__=='__main__':
head = getNode(1)
head.nextNode = getNode(2)
head.nextNode.nextNode = getNode(3)
head.nextNode.nextNode.nextNode = getNode(4)
head.nextNode.nextNode.nextNode.nextNode = getNode(5)
print("Linked list before insertion: ", end='')
printList(head)
data = 6
position = 2
head = insertPos(head, position, data)
print("Linked list after insertion of 6 at position 2: ", end = '')
printList(head)
Output
Original Linked List : 2 4 7 8
Linked List after Insertion : 2 2 4 7 8
Time Complexity: O(N), as no nested traversal is needed.
Space Complexity: O(1), as only temporary variables are being created.
Approach#2
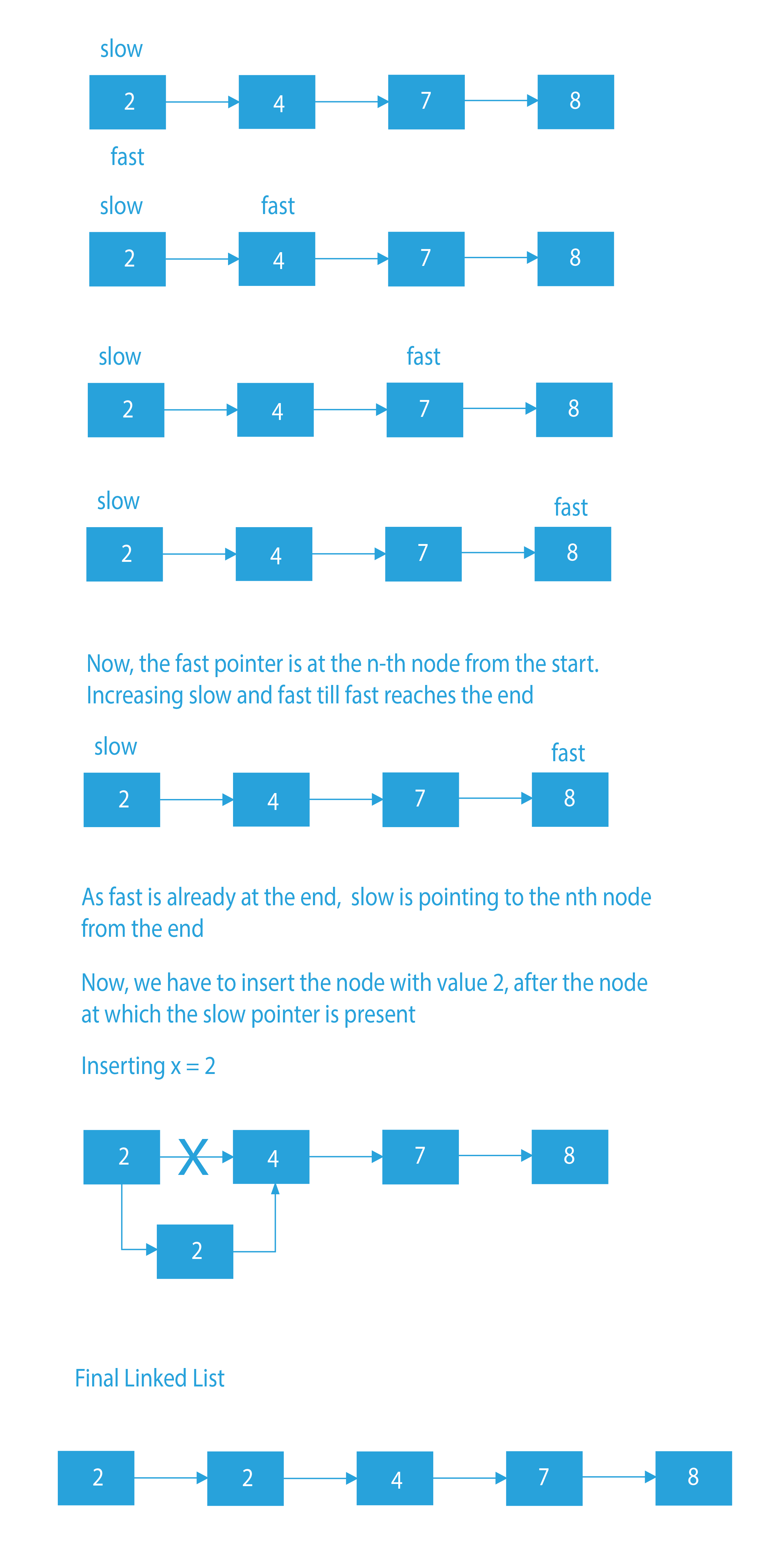
This approach uses the two pointer method. One slow pointer and another fast pointer. First, we will move the fast pointer up to the nth node from the beginning. Now, make the slow pointer point to the 1st node. Now, we will simultaneously move both the pointers. When the fast pointer reaches the end, the slow pointer will be pointing to the Nth node from the end. The best part about this approach is that it requires only a single traversal.
Algorithm
- If the linked list is empty, we will simply terminate the method.
- Create two pointers, slow and fast.
- Point the fast pointer to the Nth node from the beginning, and the slow pointer to the 1st node of the linked list.
- Simultaneously move both the pointers. When the fast pointer will reach the end, the slow pointer will be pointing to the Nth node from the end.
- Finally, insert the new node just after the slow pointer.
Dry Run
Code Implementation
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
// function to get a new node
struct Node* getNode(int data)
{
// allocate memory for the node
struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// put in the data
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
// function to insert a node after the
// nth node from the end
void insertAfterNthNode(struct Node* head, int n, int x)
{
// if list is empty
if (head == NULL)
return;
// get a new node for the value 'x'
struct Node* newNode = getNode(x);
// Initializing the slow and fast pointers
struct Node* slow_ptr = head;
struct Node* fast_ptr = head;
// move 'fast_ptr' to point to the nth node
// from the beginning
for (int i = 1; i <= n - 1; i++)
fast_ptr = fast_ptr->next;
// iterate until 'fast_ptr' points to the
// last node
while (fast_ptr->next != NULL) {
// move both the pointers to the
// respective next nodes
slow_ptr = slow_ptr->next;
fast_ptr = fast_ptr->next;
}
// insert the 'newNode' by making the
// necessary adjustment in the links
newNode->next = slow_ptr->next;
slow_ptr->next = newNode;
}
// function to print the list
void printList(struct Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
printf("%d ",head->data);
head = head->next;
}
}
// Driver program to test above
int main()
{
// Creating list 1->3->4->5
struct Node* head = getNode(1);
head->next = getNode(3);
head->next->next = getNode(4);
head->next->next->next = getNode(5);
int n = 4, x = 2;
printf("Original Linked List: ");
printList(head);
insertAfterNthNode(head, n, x);
printf("\nLinked List After Insertion: ");
printList(head);
return 0;
}
#include <bits stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* getNode(int data)
{
Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
// Function to insert the given node at
// the n-th position from the end
void insertAfterNthNode(Node* head, int n, int x)
{
if (head == NULL)
return;
Node* newNode = getNode(x);
// Initializing both the pointers
Node* slow_ptr = head;
Node* fast_ptr = head;
for (int p = 1; p <= n - 1; p++)
fast_ptr = fast_ptr->next;
// Making the fast pointer reach the end
while (fast_ptr->next != NULL) {
slow_ptr = slow_ptr->next;
fast_ptr = fast_ptr->next;
}
// Inserting the new node after the the slow pointer
newNode->next = slow_ptr->next;
slow_ptr->next = newNode;
}
void printList(Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
cout << head->data << " ";
head = head->next;
}
}
int main()
{
Node* head = getNode(2);
head->next = getNode(4);
head->next->next = getNode(7);
head->next->next->next = getNode(8);
int n = 4;
int x = 2;
cout << "Original Linked List: ";
printList(head);
insertAfterNthNode(head, n, x);
cout << "\nLinked List After Insertion: ";
printList(head);
return 0;
}
public class PrepBytes
{
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
}
static Node getNode(int data)
{
Node newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = data;
newNode.next = null;
return newNode;
}
static void insertAfterNthNode(Node head,
int n, int x)
{
if (head == null)
return;
Node newNode = getNode(x);
Node slow_ptr = head;
Node fast_ptr = head;
for (int i = 1; i <= n - 1; i++)
fast_ptr = fast_ptr.next;
while (fast_ptr.next != null)
{
slow_ptr = slow_ptr.next;
fast_ptr = fast_ptr.next;
}
newNode.next = slow_ptr.next;
slow_ptr.next = newNode;
}
static void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null)
{
System.out.print(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node head = getNode(2);
head.next = getNode(4);
head.next.next = getNode(7);
head.next.next.next = getNode(8);
int n = 4, x = 2;
System.out.println("Original Linked List: ");
printList(head);
insertAfterNthNode(head, n, x);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Linked List After Insertion: ");
printList(head);
}
}
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
def getNode(data) :
newNode = Node(0)
newNode.data = data
newNode.next = None
return newNode
# function to insert a node after the
# nth node from the end
def insertAfterNthNode(head, n, x) :
if (head == None):
return
newNode = getNode(x)
# Initializing both the pointers
slow_ptr = head
fast_ptr = head
for p in range(1, n):
fast_ptr = fast_ptr.next
# Making the fast pointer reach the end
while (fast_ptr.next != None):
slow_ptr = slow_ptr.next
fast_ptr = fast_ptr.next
# Inserting the new node after the the slow pointer
newNode.next = slow_ptr.next
slow_ptr.next = newNode
def printList( head) :
while (head != None):
print(head.data ,end = " ")
head = head.next
head = getNode(2)
head.next = getNode(4)
head.next.next = getNode(7)
head.next.next.next = getNode(8)
n = 4
x = 2
print("Original Linked List: ")
printList(head)
insertAfterNthNode(head, n, x)
print()
print("Linked List After Insertion: ")
printList(head)
Output
Original Linked List : 2 4 7 8
Linked List after Insertion : 2 2 4 7 8
Time Complexity: O(N), as no nested traversal is needed.
Space Complexity: O(1), as only temporary variables are being created.
So, in this article, we have tried to explain the most efficient approach to insert a node after the Nth node from the end. We have shown two approaches here. Both approaches take O(N) time, but the second one is more efficient as it only requires a single traversal of the list. The slow and fast pointer technique is a must-know for coding interviews.
If you want to solve more questions on Linked List, which are curated by our expert mentors at PrepBytes, you can follow this link Linked List.