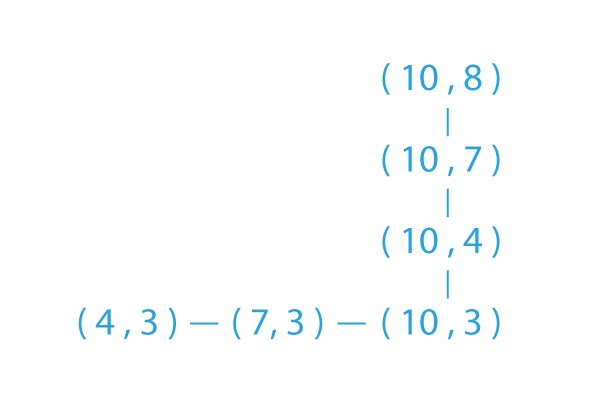Introduction
The linked list is one of the most important concepts to know while preparing for interviews. Having a good grasp of a linked list can be a huge plus point in coding interviews.
Problem Statement
In this problem, we will be given a linked list, where each node will have two integers representing the x and y coordinates of a point. We need to remove the middle points present in the line segments drawn by joining the coordinates of the node.
Problem Statement Understanding
The problem statement is quite straightforward; we have to draw line segments corresponding to the coordinates of the nodes and then remove the middle points present in each line segment.
Suppose we have a horizontal line segment formed by 6 different points, then according to the problem statement, we need to remove the four points in between the starting and ending point of the line segment and leave the starting and ending point as it is.
- We need to do the same with the lines that are vertical i.e., leave starting and ending points and remove middle points.
Let’s try to understand the problem with the help of examples:
If the linked list given to us is (4,3)→(7,3)→(10,3)→(10,4)→(10,7)→(10,8)→NULL.
- From the above graphical plot of the given linked list, we see that the first three nodes form a line segment parallel to the x-axis.
- So, the middle point in the line segment is the second node. Hence, it is removed.
- Similarly, the last three nodes form a line segment parallel to the y-axis and the last second node, and the last third node, are the points that lie in between the starting and ending point of the segment.
- Hence, both of them are removed from the list (removing middle points from line segment).
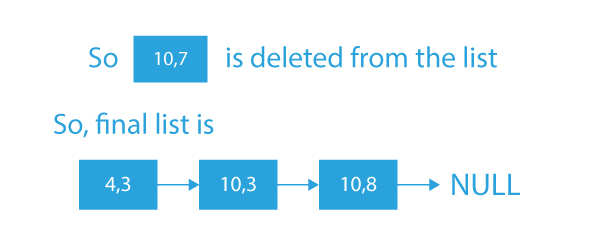
- So, after removing all the middle points from the linked list, our final resultant linked list will be: (4,3)→(10,3)→(10,8)→NULL
At this point, we have understood the problem statement. Now we will try to formulate an approach for this problem.
Before moving to the approach section, try to think about how you can approach this problem.
- If stuck, no problem, we will thoroughly see how we can approach this problem in the next section.
Let’s move to the approach section.
Approach
- We will maintain two pointers initialized by the first and second nodes of the given list, respectively.
- Now, we will iterate the list, and while iterating, we will check if two consecutive nodes have the same x or y coordinate or not.
- If that is the case, then we will remove all the nodes that have the same x or y coordinate as the first pointer and keep the second pointer at the end of the segment.
- In this way, all the middle points of the line segments will be removed, and hence our objective will be satisfied.
The approach is discussed in more depth in the algorithm section.
Algorithm
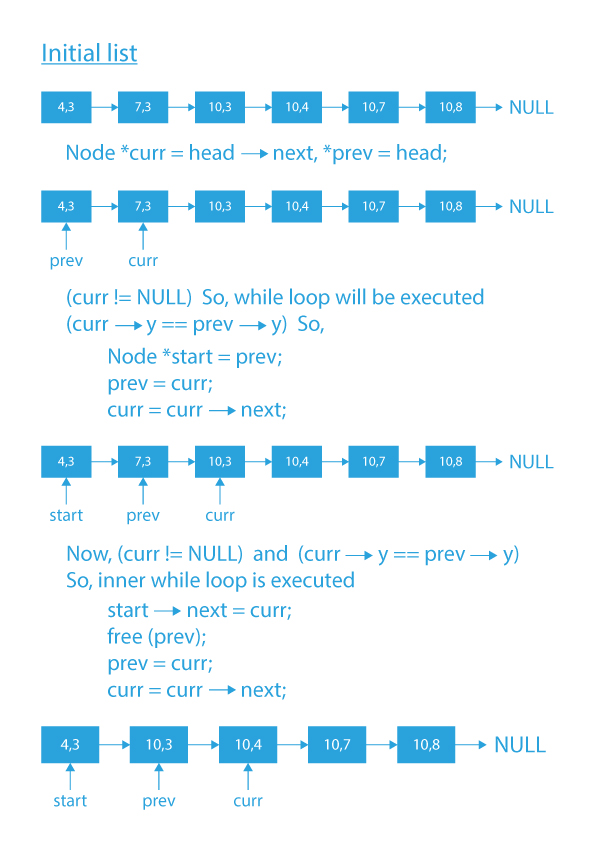
1) Initialize two pointers prev and curr with the first and second node of the list, respectively.
2) Iterate the list till curr is not NULL.
3) If the x-coordinate of curr, as well as prev, is equal (i.e., vertical line), then:
a) Create a start variable initialized to prev, which will denote the starting of the segment.
b) Move prev and curr forward by one node
c) Now, run a while loop until curr is not NULL and x-coordinates of curr and prev are equal.
d) Inside the loop, attach curr after start and delete the prev node.
e) Also, update prev to curr and move curr forward by one node.
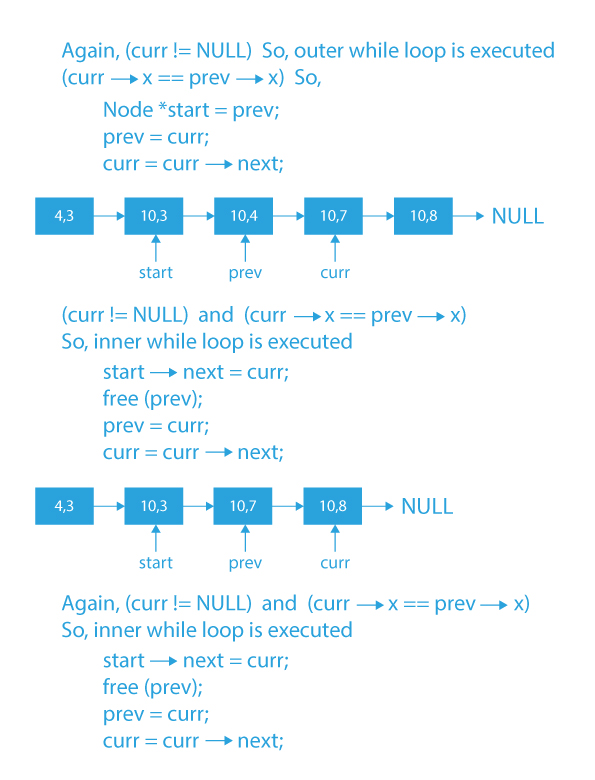
4) If the y-coordinate of curr, as well as prev, is equal (i.e., Horizontal line), then:
a) Create a start variable initialized to prev, which will denote starting of the segment.
b) Move prev and curr forward by one node.
c) Now, run a while loop until curr is not NULL and y-coordinates of curr and prev are equal.
d) Inside the loop, attach curr after start and delete the prev node.
e) Also, update prev to curr and move curr forward by one node.
5) If none of the two coordinates is equal, move forward prev and curr by one node.
Dry Run
Code Implementation
#includeusing namespace std; class Node { public: int x, y; Node *next; //constructor Node(int x,int y){ this->x = x; this->y = y; next = NULL; } }; // Using this function we will print the list void printList(Node *head) { Node *temp = head; while (temp != NULL) { printf("(%d, %d)-> ", temp->x, temp->y); temp = temp->next; } printf("NULL\n"); } // Using these functions we will delete the middle nodes from the given linked list. void delete_Middle_Nodes(Node *head) { Node *curr = head->next, *prev = head; while (curr) { // x-coordinate equality check if (curr->x == prev->x) { Node *start = prev; prev = curr; curr = curr->next; //remove the nodes in middle of //the segment parallel to y-axis while (curr && curr->x == prev->x) { start->next = curr; free(prev); prev = curr; curr = curr->next; } } // y-coordinate equality check else if (curr->y == prev->y) { Node *start = prev; prev = curr; curr = curr->next; //remove the nodes in middle of //the segment parallel to x-axis while (curr && curr->y == prev->y) { start->next = curr; free(prev); prev = curr; curr = curr->next; } } else { prev = curr; curr = curr->next; } } } int main() { Node *head = NULL; head = new Node(4,3); head->next = new Node(7,3); head->next->next = new Node(10,3); head->next->next->next = new Node(10,4); head->next->next->next->next = new Node(10,7); head->next->next->next->next->next = new Node(10,8); printf("Given Linked List: \n"); printList(head); delete_Middle_Nodes(head); printf("Modified Linked List: \n"); printList(head); return 0; }
#include#include struct Node { int x, y; struct Node *next; }; void push(struct Node ** head_ref, int x,int y) { struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); new_node->x = x; new_node->y = y; new_node->next = (*head_ref); (*head_ref) = new_node; } void printList(struct Node *head) { struct Node *temp = head; while (temp != NULL) { printf("(%d,%d)-> ", temp->x,temp->y); temp = temp->next; } printf("\n"); } void deleteNode(struct Node *head, struct Node *Next) { head->next = Next->next; Next->next = NULL; free(Next); } struct Node* deleteMiddle(struct Node *head) { // If only one node or no node...Return back if (head==NULL || head->next ==NULL || head->next->next==NULL) return head; struct Node* Next = head->next; struct Node *NextNext = Next->next ; // Check if this is a vertical line or horizontal line if (head->x == Next->x) { // Find middle nodes with same x value, and delete them while (NextNext !=NULL && Next->x==NextNext->x) { deleteNode(head, Next); // Update Next and NextNext for next iteration Next = NextNext; NextNext = NextNext->next; } } else if (head->y==Next->y) // If horizontal line { // Find middle nodes with same y value, and delete them while (NextNext !=NULL && Next->y==NextNext->y) { deleteNode(head, Next); // Update Next and NextNext for next iteration Next = NextNext; NextNext = NextNext->next; } } else // Adjacent points must have either same x or same y { puts("Given linked list is not valid"); return NULL; } // Recur for next segment deleteMiddle(head->next); return head; } // Driver program to test above functions int main() { struct Node *head = NULL; push(&head, 40,5); push(&head, 20,5); push(&head, 10,5); push(&head, 10,8); push(&head, 10,10); push(&head, 3,10); push(&head, 1,10); push(&head, 0,10); printf("Given Linked List: \n"); printList(head); if (deleteMiddle(head) != NULL); { printf("Modified Linked List: \n"); printList(head); } return 0; }
class LineSegment
{
Node head;
class Node
{
int x,y;
Node next;
Node(int x, int y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
next = null;
}
}
/* This function deletes middle nodes in a sequence of
horizontal and vertical line segments represented
by linked list. */
Node deleteMiddle()
{
// If only one node or no node...Return back
if (head == null || head.next == null ||
head.next.next == null)
return head;
Node Next = head.next;
Node NextNext = Next.next;
// check if this is vertical or horizontal line
if (head.x == Next.x)
{
// Find middle nodes with same value as x and
// delete them.
while (NextNext != null && Next.x == NextNext.x)
{
head.next = Next.next;
Next.next = null;
// Update NextNext for the next iteration
Next = NextNext;
NextNext = NextNext.next;
}
}
// if horizontal
else if (head.y == Next.y)
{
// find middle nodes with same value as y and
// delete them
while (NextNext != null && Next.y == NextNext.y)
{
head.next = Next.next;
Next.next = null;
// Update NextNext for the next iteration
Next = NextNext;
NextNext = NextNext.next;
}
}
// Adjacent points should have same x or same y
else
{
System.out.println("Given list is not valid");
return null;
}
// temporarily store the head and move head forward.
Node temp = head;
head = head.next;
// call deleteMiddle() for next segment
this.deleteMiddle();
// restore head
head = temp;
return head;
}
void push(int x, int y)
{
Node new_node = new Node(x,y);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
void printList()
{
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null)
{
System.out.print("("+temp.x+","+temp.y+")->");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println("NULL");
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
public static void main(String args[])
{
LineSegment llist = new LineSegment();
llist.push(4,3);
llist.push(7,3);
llist.push(10,3);
llist.push(10,4);
llist.push(10,7);
llist.push(10,8);
System.out.println("Given list");
llist.printList();
if (llist.deleteMiddle() != null)
{
System.out.println("Modified Linked List is");
llist.printList();
}
}
}
class LinkedList(object):
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.next = None
def deleteMiddle(self):
curr = self.head.next
prev = self.head
while curr:
if curr.x == prev.x:
start = prev
prev = curr
curr = curr.next
while curr and curr.x == prev.x:
start.next = curr
del prev
prev = curr
curr = curr.next
elif curr.y == prev.y:
start = prev
prev = curr
curr = curr.next
while curr and curr.y == prev.y:
start.next = curr
del prev
prev = curr
curr = curr.next
else:
prev = curr
curr = curr.next
def push(self, x, y):
new_node = self.Node(x, y)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while temp != None:
print ("(" + str(temp.x) + "," + str(temp.y) + ")->",end=" ")
temp = temp.next
print ("Null")
# Driver program
llist = LinkedList()
llist.push(10,8)
llist.push(10,7)
llist.push(10,4)
llist.push(10,3)
llist.push(7,3)
llist.push(4,3)
print ("Given list")
llist.printList()
llist.deleteMiddle()
print ("Modified Linked List is")
llist.printList()
Output
Given Linked List:
(4, 3)-> (7, 3)-> (10, 3)-> (10, 4)-> (10, 7)-> (10, 8)-> NULL
Modified Linked List:
(4, 3)-> (10, 3)-> (10, 8)-> NULL
Time Complexity: O(n), n is the number of nodes in the given list.
[forminator_quiz id=”5820″]
So, in this blog, we have tried to explain how you can remove middle points from a linked list where each node represents a coordinate in the XY-plane in the most optimal way. If you want to solve more questions on Linked List, which are curated by our expert mentors at PrepBytes, you can follow this link Linked List.