Introduction
We can define a linked list as a sequence of data structures which are connected through links and each node is having a pointer which points to the next node. In this article, we will learn how to delete nodes which have a greater value on right side
Problem Statement for delete nodes having greater value on right
Given a singly linked list, implement a function to delete all the nodes which have a greater valued node on the right side.
Problem Statement Understanding to delete nodes having greater value on right
Let’s understand how to delete nodes which have a greater value on right side with the help of some examples.
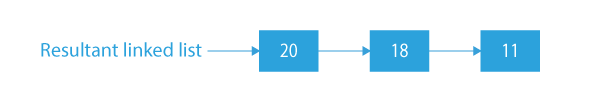
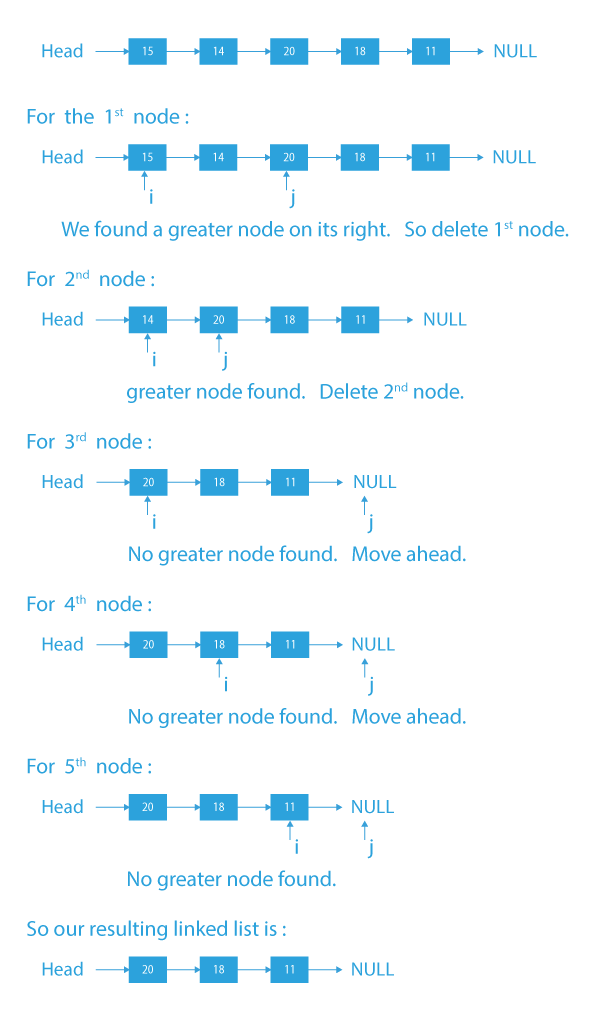
As 15 has a greater value of 20 on its right and similarly, for 14 we have 20 on its right side, these nodes will be deleted from the linked list.
For all other nodes, we don’t have a greater valued node on its right. So, they will remain on the linked list.
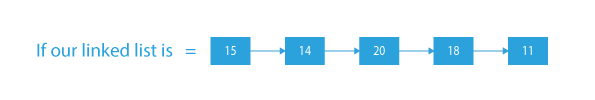
If our linked list = 1→2→3→4.
Here, each one of 1,2,3 has some number on the right which is greater than it. So, we remove them.
Only 4 has no greater valued node on its right side, so it will remain in the linked list.
I hope these examples helped you in understanding to delete nodes which have a greater value on right side
Now, can you think of an approach to delete nodes having greater value on right ?
First Approach to delete nodes having greater value on right: Brute force
One straightforward thing we can do is for each node, we traverse all the nodes on the right of it and check whether there is any node having a value greater than it or not. If yes, we simply remove that node from the linked list, or else we move to the next node.
We can implement our approach to delete nodes which have a greater value on right side using two nested ‘for loops’.
Algorithm to delete nodes having greater value on right,
- Iterate over all nodes using a loop
- For each node
- Check if there is a node on its right side with a larger value
- If yes, then delete the current node else, move forward.
Dry Run to delete nodes which have a greater value on right side
Code Implementation for delete nodes having greater value on right,:
#includeusing namespace std; struct Node { int val; Node* next; Node(int value){ val = value; next = NULL; } }; void push_front(Node** head, int new_val){ Node* new_node = new Node(new_val); new_node->next = *head; *head = new_node; } void printList(Node* head){ Node* i = head; while(i){ cout< val<<" "; i = i->next; } cout<<"\n"; } Node* reverse_it(Node* head){ Node *prev = NULL; Node *curr = head, *next; while(curr!=NULL){ next = curr->next; curr->next = prev; prev = curr; curr = next; } return prev; } void del_gr_right(Node** head){ // reverse the linked list *head = reverse_it(*head); int mx = (*head)->val; Node* prev = *head; Node* curr = (*head)->next; while(curr != NULL){ if(curr->val < mx){ // delete curr node Node* temp = curr; prev->next = curr->next; curr = curr->next; delete temp; } else { mx = max(mx, curr->val); prev = curr; curr = curr->next; } } // once again reverse it *head = reverse_it(*head); } int main(){ Node* head = NULL; push_front(&head, 11); push_front(&head, 18); push_front(&head, 20); push_front(&head, 14); push_front(&head, 15); printList(head); // 15 14 20 18 11 del_gr_right(&head); printList(head); // 20 18 11 }
#includeusing namespace std; struct Node { int val; Node* next; Node(int value){ val = value; next = NULL; } }; void push_front(Node** head, int new_val){ Node* new_node = new Node(new_val); new_node->next = *head; *head = new_node; } void printList(Node* head){ Node* i = head; while(i){ cout< val<<" "; i = i->next; } cout<<"\n"; } void del_gr_right(Node* head){ for(Node* i=head; i!=NULL;){ int value = i->val; bool found = false; for(Node* j = i->next; j!=NULL; j = j->next){ if(j->val > value){ found = 1; break; } } if(found){ // delete node i Node* temp = i->next; i->val = i->next->val; i->next = i->next->next; delete temp; } else { i = i->next; } } } int main(){ Node* head = NULL; push_front(&head, 11); push_front(&head, 18); push_front(&head, 20); push_front(&head, 14); push_front(&head, 15); printList(head); // 15 14 20 18 11 del_gr_right(head); printList(head); // 20 18 11 }
class GreaterValue {
Node head;
/* Linked list Node*/
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
/* Deletes nodes which have a node with greater value node on left side */
void delLesserNodes()
{
/* 1.Reverse the linked list */
reverseList();
/* 2) In the reversed list, delete nodes which
have a node with greater value node on left
side. Note that head node is never deleted
because it is the leftmost node.*/
_delLesserNodes();
/* 3) Reverse the linked list again to retain
the original order */
reverseList();
}
/* Deletes nodes which have greater value node(s)on left side */
void _delLesserNodes()
{
Node current = head;
Node maxnode = head;
Node temp;
while (current != null && current.next != null) {
/* If current is smaller than max, then delete
current */
if (current.next.data < maxnode.data) {
temp = current.next;
current.next = temp.next;
temp = null;
}
/* If current is greater than max, then update max and move current */
else {
current = current.next;
maxnode = current;
}
}
}
void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
void reverseList()
{
Node current = head;
Node prev = null;
Node next;
while (current != null) {
next = current.next;
current.next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
}
head = prev;
}
void printList()
{
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
GreaterValue llist = new GreaterValue();
llist.push(9);
llist.push(2);
llist.push(6);
llist.push(5);
llist.push(11);
llist.push(5);
llist.push(2);
llist.push(12);
System.out.println("Given Linked List");
llist.printList();
llist.delLesserNodes();
System.out.println("Modified Linked List");
llist.printList();
}
}
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while(temp):
print (temp.data,end=" ")
temp = temp.next
def del_gr_right(self):
i = self.head
while i:
value = i.data
found = False
j = i.next
while j:
if j.data > value:
found = True
break
j = j.next
if found:
temp = i.next
i.data = i.next.data
i.next = i.next.next
temp = None
else:
i = i.next
llist = LinkedList()
llist.push(11)
llist.push(18)
llist.push(20)
llist.push(14)
llist.push(15)
print ("Given Linked List is:")
llist.printList()
print()
llist.del_gr_right()
print ("\nLinked list after deletion is")
llist.printList()
Output
15 14 20 18 11
20 18 11
Time complexity: O(N*N), due to 2 nested for loops.
Space complexity: O(1), as we don’t use any extra space
Here, N is the total number of nodes in the given linked list.
Can we do some improvements?
If we could traverse from right to left, what improvements would it make?
Second Approach to delete nodes having greater value on right: Reversing the linked list (optimized)
We can’t traverse a linked list from right to left, let’s reverse it.
In the reversed linked list, we need to do the opposite. We have to remove all the nodes having greater value on the left. Since now, we can traverse from left to right, we can keep track of the maximum value and delete the node whose values are less than the maximum value till that node.
After performing the required deletions, we can again reverse the linked list to get the result in the correct order.
Algorithm to delete nodes having greater value on right
- Reverse the linked list.
- Now traverse the linked list and keep track of the maximum value.
- At any node, if the node’s value is smaller than the maximum value till now, delete the node.
- Now we have a linked list in which all nodes having greater value on the left side have been deleted.
- Reverse the linked list and return it as our answer.
Dry Run to delete nodes having greater value on right,
Code Implementation
#include#include /* structure of a linked list node */ struct Node { int data; struct Node* next; }; void reverseList(struct Node** headref); void _delLesserNodes(struct Node* head); void delLesserNodes(struct Node** head_ref) { reverseList(head_ref); _delLesserNodes(*head_ref); reverseList(head_ref); } void _delLesserNodes(struct Node* head) { struct Node* current = head; struct Node* maxnode = head; struct Node* temp; while (current != NULL && current->next != NULL) { if (current->next->data < maxnode->data) { temp = current->next; current->next = temp->next; free(temp); } else { current = current->next; maxnode = current; } } } void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data) { struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); new_node->data = new_data; new_node->next = *head_ref; *head_ref = new_node; } void reverseList(struct Node** headref) { struct Node* current = *headref; struct Node* prev = NULL; struct Node* next; while (current != NULL) { next = current->next; current->next = prev; prev = current; current = next; } *headref = prev; } void printList(struct Node* head) { while (head != NULL) { printf("%d ", head->data); head = head->next; } printf("\n"); } int main() { struct Node* head = NULL; push(&head, 3); push(&head, 2); push(&head, 6); push(&head, 5); push(&head, 11); push(&head, 10); push(&head, 15); push(&head, 12); printf("Given Linked List \n"); printList(head); delLesserNodes(&head); printf("Modified Linked List \n"); printList(head); return 0; }
#includeusing namespace std; struct Node { int val; Node* next; Node(int value){ val = value; next = NULL; } }; void push_front(Node** head, int new_val){ Node* new_node = new Node(new_val); new_node->next = *head; *head = new_node; } void printList(Node* head){ Node* i = head; while(i){ cout< val<<" "; i = i->next; } cout<<"\n"; } Node* reverse_it(Node* head){ Node *prev = NULL; Node *curr = head, *next; while(curr!=NULL){ next = curr->next; curr->next = prev; prev = curr; curr = next; } return prev; } void del_gr_right(Node** head){ // reverse the linked list *head = reverse_it(*head); int mx = (*head)->val; Node* prev = *head; Node* curr = (*head)->next; while(curr != NULL){ if(curr->val < mx){ // delete curr node Node* temp = curr; prev->next = curr->next; curr = curr->next; delete temp; } else { mx = max(mx, curr->val); prev = curr; curr = curr->next; } } // once again reverse it *head = reverse_it(*head); } int main(){ Node* head = NULL; push_front(&head, 11); push_front(&head, 18); push_front(&head, 20); push_front(&head, 14); push_front(&head, 15); printList(head); // 15 14 20 18 11 del_gr_right(&head); printList(head); // 20 18 11 }
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
public Node(int data){
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
class LLUtil{
public Node createLL(int[] arr){
Node head = new Node(arr[0]);
Node temp = head;
Node newNode = null;
for(int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++){
newNode = new Node(arr[i]);
temp.next = newNode;
temp = temp.next;
}
return head;
}
//This function prints given linked list
public void printLL(Node head){
while(head != null){
System.out.print(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
class GreaterValue {
public static void main (String[] args) {
int[] arr = {12,15,10,11,5,6,2,3};
LLUtil llu = new LLUtil();
Node head = llu.createLL(arr);
System.out.println("Given Linked List");
llu.printLL(head);
head = deleteNodesOnRightSide(head);
System.out.println("Modified Linked List");
llu.printLL(head);
}
public static Node deleteNodesOnRightSide(Node head){
if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
Node nextNode = deleteNodesOnRightSide(head.next);
if(nextNode.data > head.data) return nextNode;
head.next = nextNode;
return head;
}
}
class Node: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.next = None class LinkedList: def __init__(self): self.head = None def push(self, new_data): new_node = Node(new_data) new_node.next = self.head self.head = new_node def printList(self): temp = self.head while(temp): print (temp.data,end=" ") temp = temp.next def reverse_it(self): prev = None curr = self.head while curr: next = curr.next curr.next = prev prev = curr curr = next self.head = prev return prev def del_gr_right(self): self.reverse_it() temp = self.head mx = self.head.data prev = self.head curr = self.head.next while curr: if curr.data < mx: temp = curr prev.next = curr.next curr = curr.next del temp else: mx = max(mx, curr.data) prev = curr curr = curr.next self.reverse_it() llist = LinkedList() llist.push(11) llist.push(18) llist.push(20) llist.push(14) llist.push(15) llist.printList() llist.del_gr_right() print() llist.printList()
Output
15 14 20 18 11
20 18 11
Time complexity: O(N), as we are traversing the linked list (three times).
In this article, we have seen how to delete nodes that have a greater value on the right by two different approaches. All these concepts and approaches are good for strengthening your concepts in LinkedList and can help to prepare well for the interviews. If you want to get your hands on more on linked list , you can pratice from hereLinked List.
FAQs
- Why is deletion easier in a doubly linked list?
- Is delete a keyword in java?
- What is the time complexity of deleting a node from the stack?
In a singly linked list deletion requires a pointer to the node and also to delete the previous node but in a doubly linked list, it only requires deleting the pointer.
No delete is not a keyword in java.
It requires O(n) time to delete the node from the stack.