Concepts Used
Depth First Search, Disjoint Set
Difficulty Level
Medium
Problem Statement :
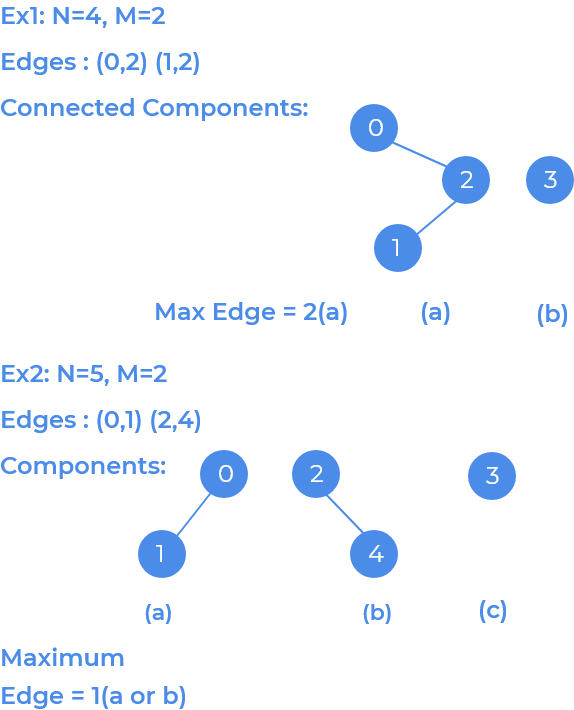
Given
Nnumber of vertices,Mnumber of edges and relation between them to form an undirected graph, our task is to find the maximum number of edges among all the connected components in the given graph.
Solution Approach :
Introduction :
Idea is to traverse the graph and count the edges for every connected component (refer to the connected components article) and print the maximum edge count.
This can be done using dfs or Disjoint Set.
Method 1 (Using DFS) :
We will traverse for every vertex
vusing dfs(), keep track whether it is visited or not usingvisited[]array of boolean type. Ifvis un-visited we will mark it visited (visited[v]=true), then traverse for all the adjacent vertices ofv, for each adjacent vertexa, we will increment edge count by1and ifais un-visited, recursive call dfs(a).Now after the first dfs() call a single connected component has been visited and it will return number of edges of this component, this process will be repeated for all vertices and every time it will return the number of edges of some component. One important thing to notice is that it will return twice the actual edge count (why? refer to Handshaking Lemma), so we need to divide edge count by
2to get the actual number of edges. We will store the maximum of all the edge count and print it.
Method 2 (Using Disjoint Set):
Although main idea behind the solution approach remains un-changed. We are going to use Disjoint Set Union or DSU data structure as an alternate way to solve our problem. DSU data structure is also sometimes called Union-Find Set. This data structure is used to keep track of the different disjoint sets.
It basically performs two operations :
- Union : It takes two vertices and join them in a single set (if it is not already there).
- Find : Determines in which subset the element is.
We are using an additional arraysize[]to keep the size of the edges for each root of our set.ithindex ofsize[]will give us the number of edges in the tree rooted withi.
We will perform union for every edge. After processing all the edges iterate throughsize[]and print the maximum value i.e maximum edge count.
Algorithms :
dfs() :
- for every vertex
v, we will mark the vertexvas visited (visited[v]= true).- Iterate for all the adjacent vertices of
vand for every adjacent vertexa, do following :
- increment the edge_count by
1.- if
ais not visited i.evisited[a]= false,
recursively call dfs(a).
- return edge_count.
union() :
- For two vertices
u&v, find the root for both vertices using find() (a=find(u)&b = find(v)).- If the root of
u&vare not similar, check the level ofa&bas follows:
- if (
level[a]>* else if (level[a]>level[b]), updateparent[b] = a&size[a]+=size[b]+1`.- else , update
parent[b]=a, updatelevel[a] = level[a]+1&size[a]+=1
find() :
- If
(parent[v]==v), returns the vertexv(which is root).- Else, update
parent[v]by recursively looking up the tree for the root.(find(parent[v])).
Complexity Analysis:
The time complexity of the first method is represented in the form of
O(V+E), whereVis the number of verices andEis the number of edges.The space complexity of the algorithm is
O(V)forvisited[]&colour[]array.
Solutions:
#include<stdio.h>
long rank[100001]={0},parent[100001]={0},size[100001]={0};
long rp(long num)
{
if(parent[num]!=num)
return (parent[num]=rp(parent[num]));
else return num;
}
void uni(long a,long b)
{
long parenta,parentb;
parenta=rp(a);
parentb=rp(b);
if(parenta==parentb)
{
size[parenta]++;
return;
}
if(rank[parenta]==rank[parentb])
{
parent[parentb]=parenta;
size[parenta]+=size[parentb]+1;
rank[parenta]++;
}
else if(rank[parentb]>rank[parenta])
{
parent[parenta]=parentb;
size[parentb]+=size[parenta]+1;
}
else if(rank[parenta]>rank[parentb])
{
parent[parentb]=parenta;
size[parenta]+=size[parentb]+1;
}
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
long i,n,m,a,b,max=-1,j;
for(i=0;i<=100000;i++)
{
parent[i]=i;
rank[i]=0;
size[i]=0;
}
scanf("%ld%ld",&n,&m);
for(i=0;i<m;i++)
{
scanf("%ld%ld",&a,&b);
uni(a,b);
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
if(size[i]>max)
{
max=size[i];
j=i;
}
printf("%ld\n",max);
}
return 0;}
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<int>v[100005];
bool vis[100005];
int siz,edges;
int dfs(int i)
{
vis[i]=true;
//siz++;
for(int u:v[i])
{
edges++;
if(!vis[u])
dfs(u);
}
return edges;
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
v[i].clear();
vis[i] = false;
}
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
v[a].push_back(b);
v[b].push_back(a);
}
siz=0,edges = 0;
int maxedges=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(!vis[i])
{
//dfs(i);
//cout<<edges/2<<"\n";
maxedges=max(maxedges,dfs(i)/2);
siz=0;edges=0;
}
}
cout<<maxedges<<"\n";
}
return 0;
}
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int t = sc.nextInt();
while(t-->0)
{
int n=sc.nextInt();
int m=sc.nextInt();
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> g=new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++)
g.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
int u=sc.nextInt();
int v=sc.nextInt();
g.get(u).add(v);
g.get(v).add(u);
}
int max=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
boolean vis[]=new boolean[n+1];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(!vis[i]){
int res=(dfs(g,i,vis));
max=Math.max(res/2,max);
}
}
System.out.println(max);
}
}
static int dfs(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> g,int s,boolean vis[]){
int edge=g.get(s).size();
vis[s]=true;
for (int i=0;i<g.get(s).size();i++) {
if (vis[g.get(s).get(i)]==false){
edge+=dfs(g,g.get(s).get(i),vis);
}
}
return edge;
}
}
[forminator_quiz id="1944"]
This article tried to discuss Depth First Search, Disjoint Set. Hope this blog helps you understand and solve the problem. To practice more problems on Depth First Search, Disjoint Set you can check out .