Concepts Used
Breadth First Search, Disjoint Set
Difficulty Level
Easy
Problem Statement :
Given an undirected graph, print Yes if a cycle is present in the graph else print No.
Solution Approach :
Introduction :
Cycle in a graph means there’s a loop in between its edges.
If we traverse a graph and after visited certain vertices we reach the vertex from where we have started, then the graph is said to have a cycle or a loop.For every visited vertex
v, when we have found any adjacent vertexu, such thatuis already visited, anduis not the parent of vertexv. Then one cycle is detected.
This problem can be solved by many ways like Breadth First Search, Depth First Search or Disjoint Set.
Method 1 (Using BFS) :
In this method we are going to use Breadth First Search or BFS to find cycle in a graph. In dfs for each vertex
vwe iterate through all its adjacent vertices and for each vertexaand mark it visited, further makevthe parent ofa(so that parent is not considered for cycle).If there is any vertex
awhich is already visited earlier, then we check if it is the parent ofaor not. If not, then there exist a cycle.
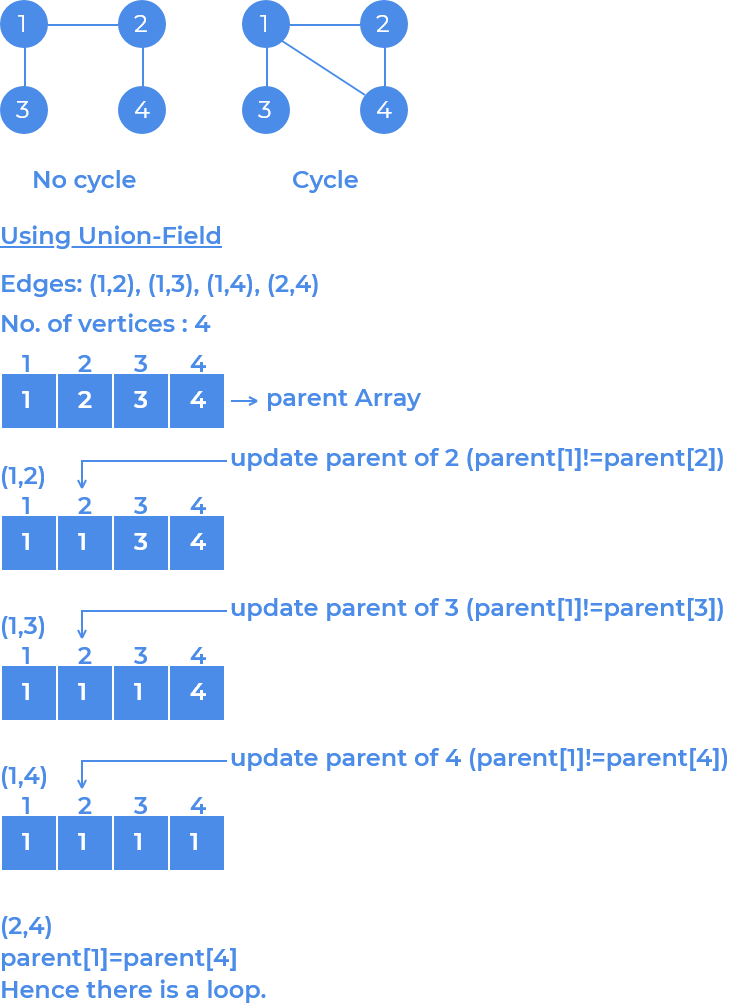
Method 2 (Using Disjoint Set) :
Disjoint Set Union or DSU data structure is also sometimes called Union-Find Set. This data structure is used to keep track of the different disjoint sets.
It basically performs two operations :
- Union : It takes two vertices and join them in a single set (if it is not already there).
- Find : Determines in which subset the element is.
We will use a
parent[]array to keep track of the parents of each vertex.ithelement will store the root/parent ofithvertex. Now for every edge (uv) , check if the root ofuandvis same using find(), if the root is same then there exist a cycle. If not, perform union() with both vertices to update theparent[]array.How is the above approach actually working?
Each disjoint set stores the vertices which are connected (directly or indirectly) to each other and has no relation/connection with any other vertex (as it is non overlapping set), so if there is any pair of vertices (edge) which belongs to the same set this will create a cycle in the graph as they belong to the same root vertex and they are also connected with each other.
Algorithms :
union() :
- For two vertices
u&v, find the root for both vertices using find() (a=find(u)&b = find(v)).- If the root of
u&vare not similar, check the level ofa&bas follows:
- if (
level[a]>* else if (level[a]>level[b]), updateparent[b] = a`.- else , update
parent[b]=a& updatelevel[a] = level[a]+1find() :
- If
(parent[v]==v), returns the vertexv(which is root).- Else, update
parent[v]by recursively looking up the tree for the root.(find(parent[v])).
Complexity Analysis:
The time complexity of Breadth First Search is represented in the form of
O(V + E), whereVis the number of nodes andEis the number of edges.The space complexity of the algorithm is
O(V)as it requires two arrays ( visited[ ] & parent[ ]) of sizeV.Talking about Union-Find data structure, since we have used path compression & union by level (refer to Disjoint Set article for more detailed explanation), we will reach nearly constant time
O(1)for each query. It turns out, that the final amortized time complexity isO(α(V)), whereα(V)is the inverse Ackermann function, which grows very slowly(α(V)<5). In our case a single call might takeO(logn)in the worst case, but if we do m such calls back to back we will end up with an average time ofO(α(n)).
Solutions:
#include<stdio.h>
int findd(int parent[],int i)
{
if(parent[i]==i)
return i;
return parent[i] = findd(parent, parent[i]);
}
void unionn(int parent[],int level[],int i,int j)
{
int a = findd(parent,i);
int b = findd(parent,j);
if(level[a]<level[b])
parent[a]=b;
else if(level[a]>level[b])
parent[b]=a;
else{
parent[b]=a;
level[a]++;
}
}
int main()
{
int n,m,flag=1;
scanf("%d %d", &n,&m);
int parent[n+1],level[n+1];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{parent[i]=i;level[i]=0;}
while(m--)
{
int u,v;
scanf("%d %d", &u,&v);
u +=1;
v +=1;
int a = findd(parent,u);
int b = findd(parent,v);
if(a==b)
{
flag = 0;
break;
}
unionn(parent,level,u,v);
}
if(flag!=1)
printf("%s\n","Yes");
else
printf("%s\n","No");
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int findd(int parent[],int i)
{
if(parent[i]==i)
return i;
return parent[i] = findd(parent, parent[i]);
}
void unionn(int parent[],int level[],int i,int j)
{
int a = findd(parent,i);
int b = findd(parent,j);
if(level[a]<level[b])
parent[a]=b;
else if(level[a]>level[b])
parent[b]=a;
else{
parent[b]=a;
level[a]++;
}
}
int main()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
int parent[n+1],level[n+1]={0};
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{parent[i]=i;level[i]=0;}
string ans = "No";
while(m--)
{
int u,v;
cin>>u>>v;
u +=1;
v +=1;
int a = findd(parent,u);
int b = findd(parent,v);
if(a==b)
{
ans = "Yes";
break;
}
unionn(parent,level,u,v);
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
public static void main(String arg[])
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int V = sc.nextInt();
int e = sc.nextInt();
ArrayList <Integer> adj[] = new ArrayList[V];
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
adj[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
while(e-->0)
{
int u = sc.nextInt();
int v = sc.nextInt();
addEdge(adj, u,v);;
}
if (isCyclicDisconntected(adj, V) == true)
System.out.println("Yes");
else
System.out.println("No");
}
static void addEdge(ArrayList<Integer> adj[], int u, int v)
{
adj[u].add(v);
adj[v].add(u);
}
static boolean isCyclicConntected(ArrayList<Integer> adj[], int s,int V, boolean visited[])
{
// Set parent vertex for every vertex as -1.
int parent[] = new int[V];
Arrays.fill(parent, -1);
// Create a queue for BFS
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
// Mark the current node as
// visited and enqueue it
visited[s] = true;
q.add(s);
while (!q.isEmpty())
{
int u = q.poll();
for (int i=0; i<adj[u].size();i++)
{
int v = adj[u].get(i);
if (!visited[v])
{
visited[v] = true;
q.add(v);
parent[v] = u;
}
else if (parent[u] != v)
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
static boolean isCyclicDisconntected(ArrayList<Integer> adj[], int V)
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
boolean visited[] = new boolean[V];
Arrays.fill(visited,false);
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (!visited[i] &&
isCyclicConntected(adj, i, V, visited))
return true;
return false;
}
}
[forminator_quiz id="1934"]
This article tried to discuss Breadth First Search, Disjoint Set. Hope this blog helps you understand and solve the problem. To practice more problems on Breadth First Search, Disjoint Set you can check out .