Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate and individuals consume digital services. The cloud offers unparalleled scalability, cost efficiency, and accessibility, enabling organizations to focus on their core competencies while leveraging powerful computing resources. However, the rapid growth and adoption of cloud computing have brought forth a unique set of challenges. In this article, we will explore the top challenges of cloud computing that organizations face in today’s digital landscape.
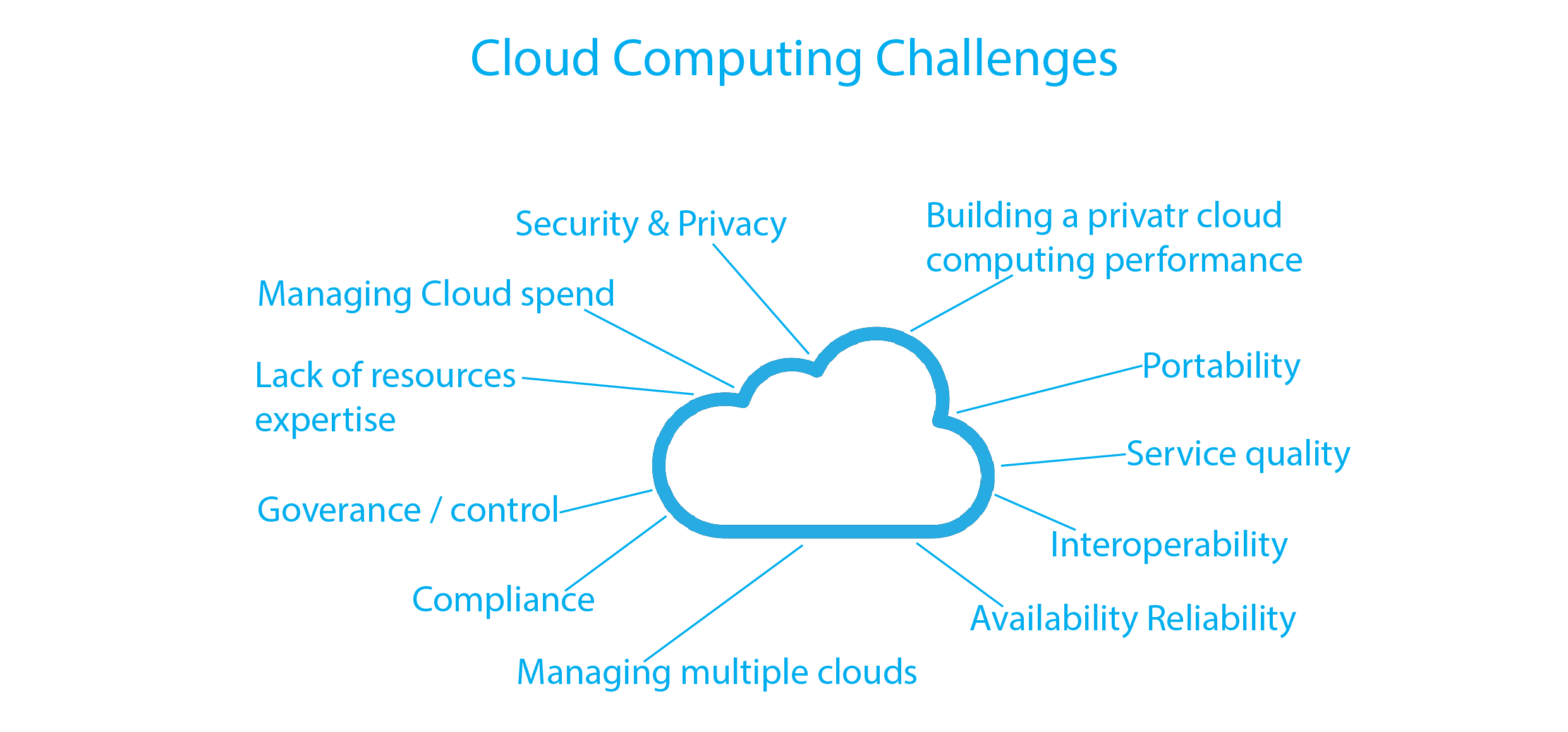
Challenges of Cloud Computing
-
Security and Data Privacy
Security remains one of the primary concerns for cloud computing users. Entrusting sensitive data to third-party service providers requires robust security measures to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and other malicious activities. While cloud providers invest heavily in security infrastructure, it is crucial for organizations to implement additional security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and data backup strategies. Compliance with data privacy regulations, like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), poses an additional challenge for organizations operating across multiple jurisdictions. -
Downtime and Service Reliability
Cloud service disruptions can have severe implications for businesses heavily dependent on cloud infrastructure. Downtime can result from technical glitches, network outages, or even natural disasters affecting data centers. Organizations must assess the reliability and uptime guarantees provided by cloud service providers to ensure minimal disruptions to their operations. Implementing disaster recovery plans, including data backup and redundancy strategies, is crucial to mitigating the risks associated with service interruptions. -
Vendor Lock-In
The adoption of a specific cloud service provider’s platform and services can lead to vendor lock-in, where switching to an alternative provider becomes challenging. Proprietary formats, data structures, and APIs can make it difficult to migrate applications and data seamlessly. Organizations should carefully consider the long-term implications and potential exit strategies before committing to a particular cloud provider to avoid being tied down to a single vendor. -
Cost Management and Optimization
While cloud computing offers cost advantages over traditional on-premises infrastructure, the pay-as-you-go model can lead to unexpected costs if not managed effectively. Cloud services’ pricing structures can be complex, involving various factors such as storage, data transfer, and computational resources. Organizations need to closely monitor and optimize their cloud resource usage to avoid over-provisioning and unnecessary expenses. Implementing automated scaling and cost management tools can help optimize resource allocation and control cloud expenditures. -
Performance and Latency
The performance of cloud-based applications is heavily dependent on network connectivity and latency. Depending on the geographical location of cloud data centers, users may experience latency issues, which can impact the user experience and application responsiveness. Organizations with stringent performance requirements must consider factors like data center locations, content delivery networks (CDNs), and application design to minimize latency and ensure optimal performance. -
Compliance and Legal Issues
As cloud computing operates on a global scale, organizations face challenges related to compliance with different legal frameworks and regulations. Industries such as healthcare, finance, and government have specific data privacy and security requirements that may conflict with cloud service providers’ practices. Organizations need to navigate complex legal landscapes, ensure contractual agreements meet regulatory standards, and maintain compliance with industry-specific regulations to mitigate legal risks and potential liabilities.
Conclusion
Cloud computing offers tremendous benefits, but it also presents a unique set of challenges that organizations must address. By proactively addressing security concerns, ensuring service reliability, managing costs, and optimizing performance, organizations can harness the full potential of cloud computing. Strategic planning, risk assessment, and careful vendor selection are crucial to overcoming the challenges associated with cloud computing. As technology continues to evolve, it is essential for organizations to stay informed and adapt their strategies to thrive in the dynamic cloud computing landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the difference between public, private, and hybrid clouds?
Public clouds are owned and operated by third-party service providers, offering computing resources to multiple organizations over the internet. Private clouds, on the other hand, are dedicated infrastructures operated solely by a single organization. Hybrid clouds combine both public and private clouds, allowing organizations to leverage the benefits of both environments. They provide greater flexibility and control over data, with the ability to scale resources dynamically.
Q2. How can I ensure the security of my data in the cloud?
Data security in the cloud requires a multi-layered approach. Start by carefully selecting a reputable cloud service provider with robust security measures and compliance certifications. Implement strong access controls, encryption mechanisms, and regularly monitor and update security configurations. Additionally, consider data backup and disaster recovery plans to ensure data availability and integrity in the event of any unforeseen events.
Q3. Can cloud computing help reduce costs for my organization?
Cloud computing can offer significant cost savings. By moving to the cloud, organizations can eliminate the need for upfront investments in hardware, software licenses, and maintenance. The pay-as-you-go pricing model allows for flexible resource allocation, enabling organizations to scale up or down as needed, avoiding overprovisioning. However, effective cost management, monitoring, and optimization strategies are crucial to ensuring that cloud expenses are optimized and aligned with actual usage.
Q4. What are the potential risks of vendor lock-in in cloud computing?
Vendor lock-in occurs when an organization becomes overly dependent on a specific cloud service provider, making it challenging to switch to an alternative provider. This can limit flexibility, hinder innovation, and increase costs. To mitigate this risk, it is essential to carefully evaluate the cloud provider’s offerings, compatibility with industry standards, and consider implementing multi-cloud or hybrid cloud strategies that allow for greater interoperability and portability.
Q5. How can cloud computing benefit small businesses?
Cloud computing offers numerous benefits for small businesses. It provides access to enterprise-level computing resources at affordable prices, eliminating the need for significant upfront investments. Small businesses can leverage scalable infrastructure, storage, and software services, enabling them to focus on their core operations without worrying about managing complex IT infrastructure. Cloud-based collaboration tools and mobility support also enhance productivity and flexibility for remote teams.