CONCEPTS USED:
Recursion
DIFFICULTY LEVEL:
Medium
PROBLEM STATEMENT(SIMPLIFIED):
Given two characters
C1,C2and an integerK, print all the possible
Klength combinations of both the characters. Print the combinations lexicographically.NOTE:
Characters can be repeated.
Consecutive
C2characters are not allowed.
For Example:
Can we use Recursion here ?
Yes, here we need to find combinations that satisfy the given conditions.
Recursionis a good choice to find all such combinations.
SOLVING APPROACH:
- Initialize an empty string
strand recursively keep adding charactersC1andC2to it based on the following cases :
If
stris empty, you can add eitherC1orC2.If
stris not empty, check if the last character isC2or not. If it isC2, you can add onlyC1as consecutiveC2'sare not allowed. If it isC1, you can add eitherC1orC2.Keep adding characters till length of
strbecomes equal toKand then printstr.
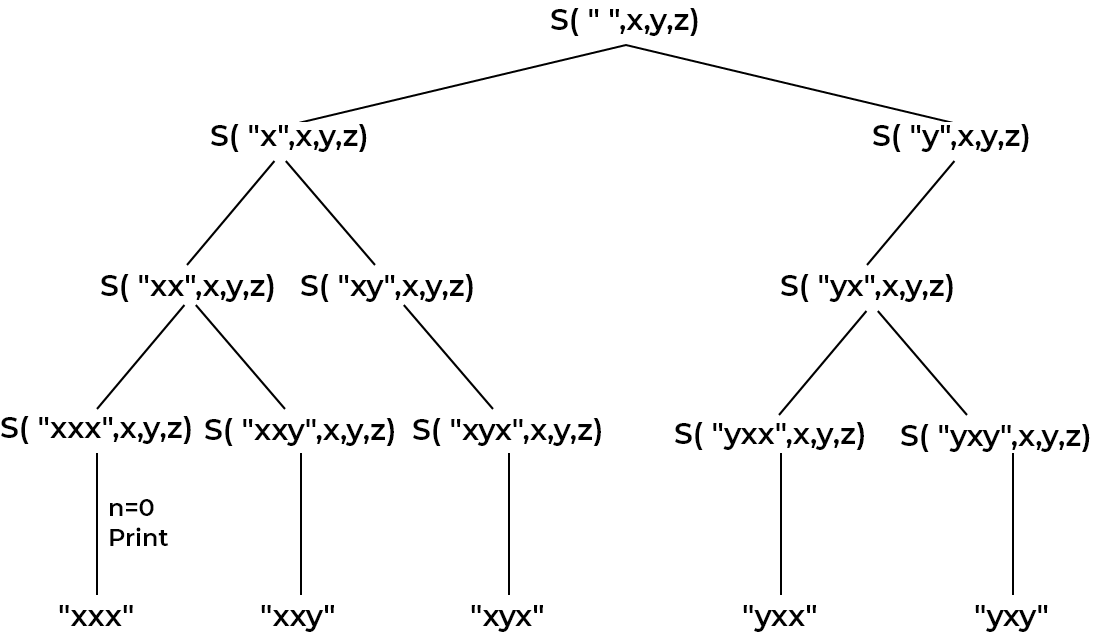
STATE SPACE TREE:
SOLUTIONS:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
/* function for appending a char to a char array */
void append(char* s, char c) {
int len = strlen(s);
s[len] = c;
s[len+1] = '\0';
}
void solve(char *s, char a, char b, int n){
if(n == 0){
printf("%s\n", s);
return;
}
else if(n > 0){
int size = strlen(s);
/* creating temporary char arrays */
char temp_a[10];
char temp_b[10];
/* copying original char array to temp arrays */
strcpy(temp_a, s);
strcpy(temp_b, s);
/* append char a and b to char arrays */
append(temp_a, a);
append(temp_b, b);
char empty[2] = "";
if(strcmp(s, empty) == 0){ //If string is empty start with any character
solve(temp_a, a, b, n-1);
solve(temp_b, a, b, n-1);
}
else{ //If string is not empty check if the last char was b or not
if(s[size - 1] == b){ // If it is b then go solving with a else solve with both
solve(temp_a, a, b, n-1);
}
else{
solve(temp_a, a, b, n-1);
solve(temp_b, a, b, n-1);
}
}
}
}
int main(){
int t; scanf("%d", &t);
while(t--){
char a,b; scanf(" %c %c", &a, &b);
int n; scanf("%d", &n);
char s[10] = "";
solve(s, a, b, n);
}
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void solve(string s,char a,char b,int n){
if(n > 0){
if(s == ""){ //If string is empty start with any character
solve(s+ a,a,b,n-1);
solve(s+ b,a,b,n-1);
}
else{ //If string is not empty check if the last char was b or not
if(s[s.size()-1]==b){ // If it is b then go solving with a else solve with both
solve(s + a,a,b,n-1);
}
else{
solve(s + a,a,b,n-1);
solve(s + b,a,b,n-1);
}
}
}
else if(n == 0)
cout<<s<<"\n";
}
int main(){
int t;cin>>t;
while(t--){
char a,b;cin>>a>>b;
int n;cin>>n;
string s = "";
solve(s,a,b,n);
}
return 0;
}
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
static void combine(String s,char a,char b,int n){
if(n > 0){
if(s == ""){ //If string is empty start with any character
combine(s+ a,a,b,n-1);
combine(s+ b,a,b,n-1);
}
else{ //If string is not empty check if the last char was b or not
if(s.charAt(s.length()-1)==b){ // If it is b then go solving with a else solve with both
combine(s + a,a,b,n-1);
}
else{
combine(s + a,a,b,n-1);
combine(s + b,a,b,n-1);
}
}
}
else if(n == 0)
System.out.println(s);
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int t = sc.nextInt();
while(t!=0){
char a = sc.next().charAt(0);
char b = sc.next().charAt(0);
int n = sc.nextInt();
String s = "";
combine(s,a,b,n);
t--;
}
}
}
def solve(s, a, b, n): if(n > 0): if(s == ""): solve(s + a, a, b, n-1) solve(s + b, a, b, n-1) else: if(s[len(s)-1] == b): solve(s + a, a, b, n-1) else: solve(s + a, a, b, n-1) solve(s + b, a, b, n-1) elif(n == 0): print(s) for _ in range(int(input())): a, b, n = input().split() n = int(n) s = "" solve(s, a, b, n)
[forminator_quiz id="1545"]
So, in this blog, we have tried to explain the concept of Recursion. If you want to solve more questions on Recursion, which are curated by our expert mentors at PrepBytes, you can follow this link Recursion.