This article will discuss in detail how to convert binary tree to doubly linked list. Conversion of binary tree to doubly linked list is an amazing task, which will improve your data structures skills that will help you to achieve your aim. Let’s discuss how to convert convert binary tree to doubly linked list.
How To Convert Binary Tree To Doubly Linked List
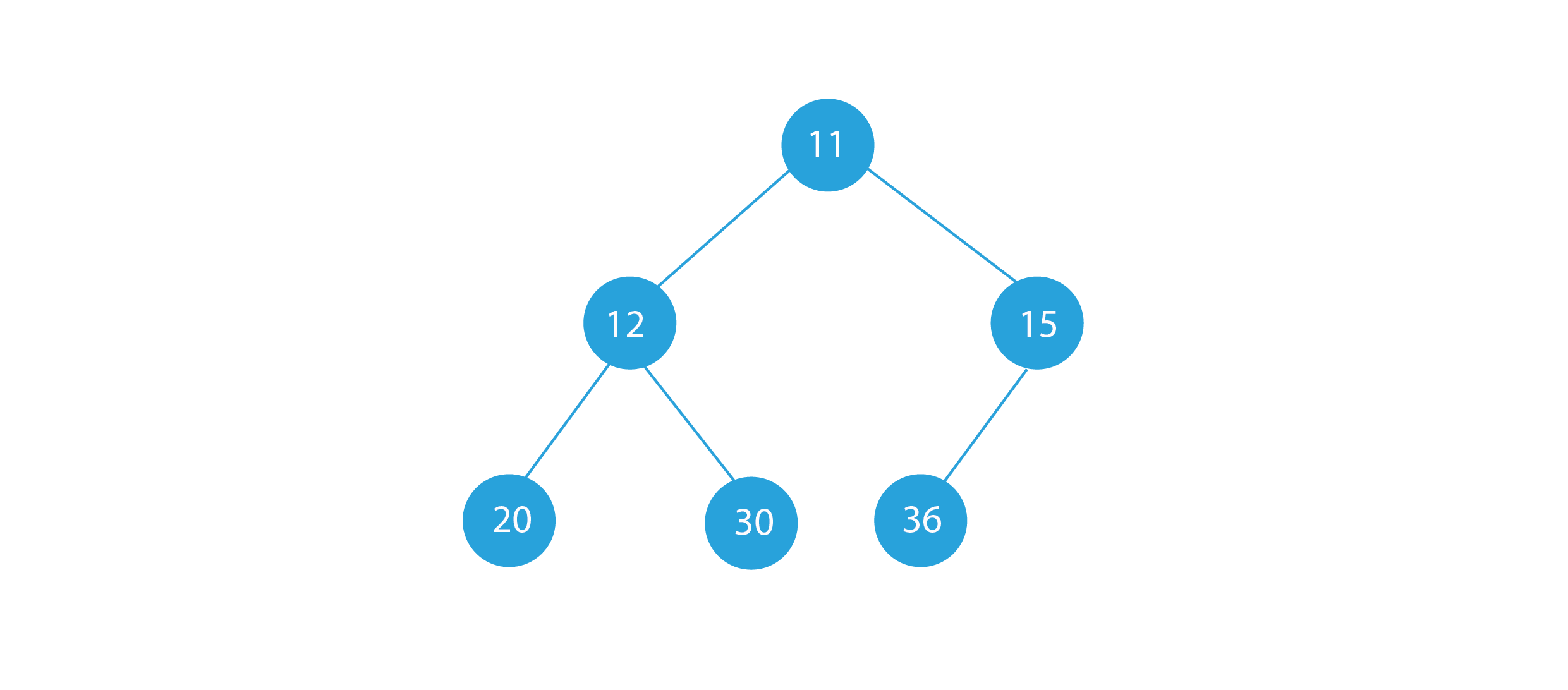
In this problem, we are given a binary tree. We have to convert the given binary tree to a doubly-linked list.
We have to store the inorder traversal of the given binary tree in the newly created linked list.
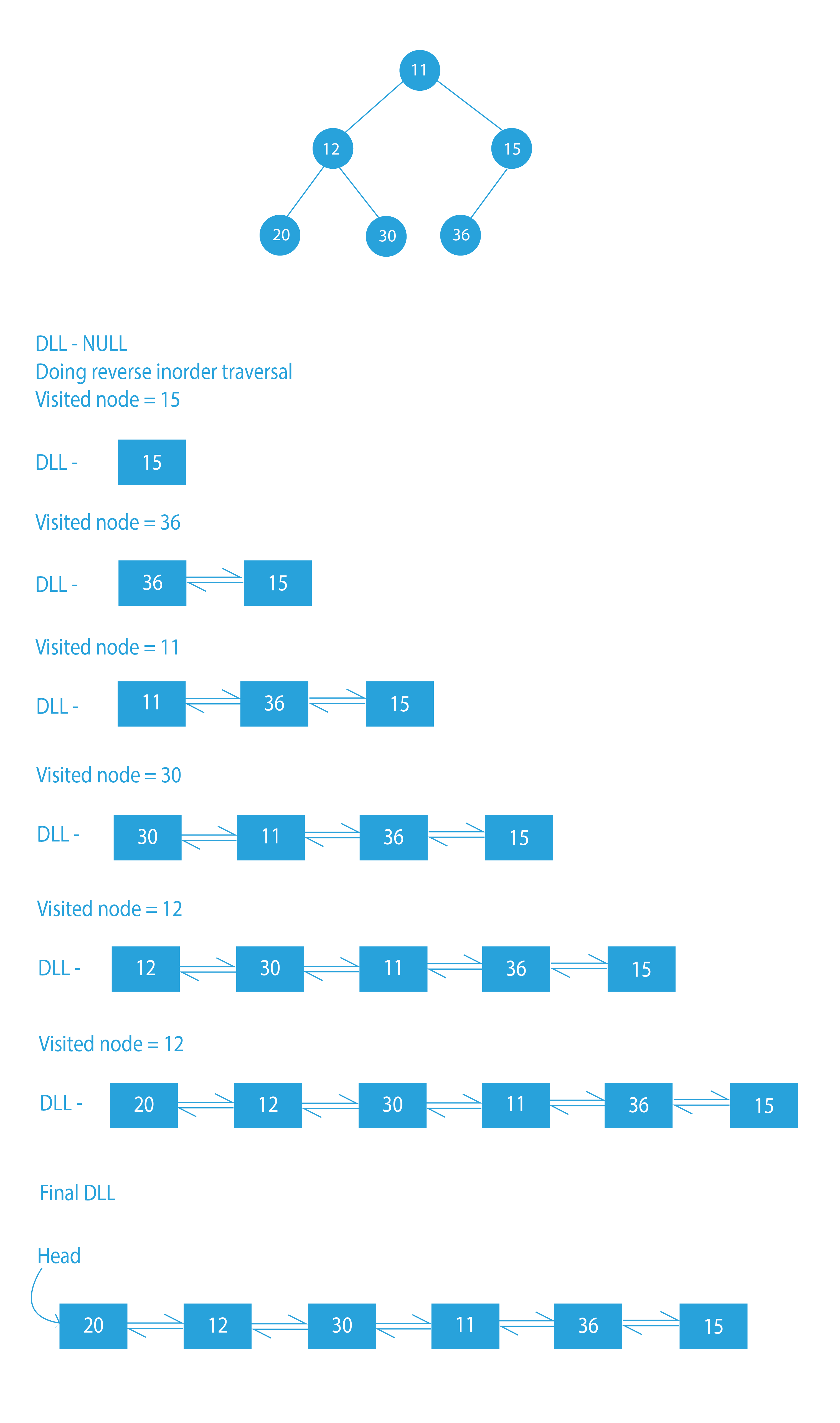
Sample Input:
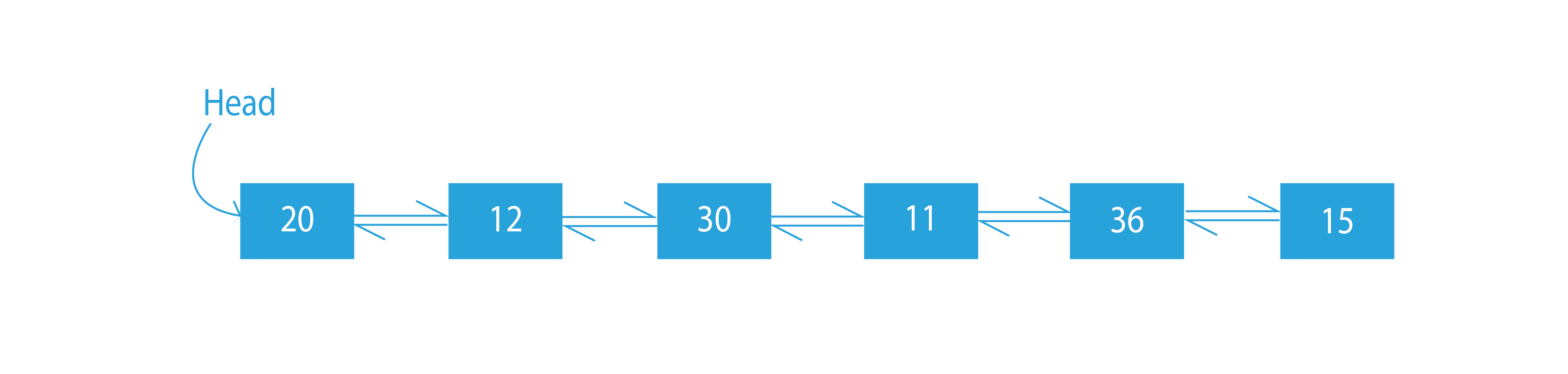
Sample Output:
Explanation:
The output doubly linked list contains the in-order traversal of the given binary tree.
We should note that the order of the nodes in the doubly linked list must be the same as the in-order traversal of the binary tree. The first node of the in-order traversal must be the head of the doubly linked list. The left and right pointers will be used as previous and next pointers, respectively. Let us have a glance at the approach.
Approach#1 To Convert Binary Tree To Doubly Linked List
In this approach, we will traverse do an inorder traversal of the binary tree. We will add the nodes at the beginning of the newly created linked list, and update the head every time. But there is a problem. Since we will insert at beginning, the order or the linked list that we will recieve, will be reversed.
To correct that, we can do a reverse inorder traversal of the tree, i.e. we will traverse through the right subtree before the left subtree.
Algorithm To Convert Binary Tree To Doubly Linked List
- Base Case – If the root is NULL, then simply return.
- Recur for the right subtree.
- Make the current root’s right point to head, and head’s left pointer to the the current root. By doing this, we are adding the current root to the head , and make the current root the head.
- After the above step, recur for the left subtree.
- Recursively, the tree will be traversed and the doubly linked list will be created as discussed.
Dry run To Convert Binary Tree To Doubly Linked List
Code Implementation To Convert Binary Tree To Doubly Linked List
#include#include struct Node { int data; struct Node *left; struct Node *right; }; struct Node* newNode(int data) { struct Node *node = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); node->data = data; node->left = node->right = NULL; return node; } void BToDLL(struct Node* root,struct Node* head) { if (root == NULL) return; BToDLL(root->right, head); root->right = head; if (head != NULL) head->left = root; head = root; BToDLL(root->left, head); } void printList(struct Node* head) { printf("Extracted Doubly Linked list is:\n"); while (head) { printf("%d ", head->data); head = head->right; } } int main() { struct Node* root = newNode(11); root->left = newNode(12); root->right = newNode(15); root->left->left = newNode(20); root->left->right = newNode(30); root->right->left = newNode(36); struct Node* head = NULL; BToDLL(root, head); printList(head); return 0; }
#includestruct Node { int data; Node *left, *right; }; Node* newNode(int data) { Node* node = new Node; node->data = data; node->left = node->right = NULL; return node; } void BToDLL(Node* root, Node*& head) { if (root == NULL) return; BToDLL(root->right, head); root->right = head; if (head != NULL) head->left = root; head = root; BToDLL(root->left, head); } void printList(Node* head) { printf("Extracted Doubly Linked list is:\n"); while (head) { printf("%d ", head->data); head = head->right; } } int main() { Node* root = newNode(11); root->left = newNode(12); root->right = newNode(15); root->left->left = newNode(20); root->left->right = newNode(30); root->right->left = newNode(36); Node* head = NULL; BToDLL(root, head); printList(head); return 0; }
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree {
Node root;
Node head;
void BToDLL(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
return;
BToDLL(root.right);
root.right = head;
if (head != null)
head.left = root;
head = root;
BToDLL(root.left);
}
void printList(Node head)
{
System.out.println("Extracted Doubly Linked List is : ");
while (head != null) {
System.out.print(head.data + " ");
head = head.right;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(11);
tree.root.left = new Node(12);
tree.root.right = new Node(15);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(20);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(30);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(36);
tree.BToDLL(tree.root);
tree.printList(tree.head);
}
}
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.right = None
self.data = data
self.left = None
class BtoDll:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.tail = None
def convert(self, root):
if root is None:
return
self.convert(root.left)
node = root
if self.head is None:
self.head = node
else:
self.tail.right = node
node.left = self.tail
self.tail = node
self.convert(root.right)
return self.head
def BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root):
converter = BtoDll()
return converter.convert(root)
def print_dll(head):
while head is not None:
print(head.data, end=" ")
head = head.right
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = Node(11)
root.left = Node(12)
root.right = Node(15)
root.left.left = Node(20)
root.left.right = Node(30)
root.right.left = Node(36)
head = BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root)
print("Extracted Doubly Linked list is:")
print_dll(head)
Output :
Extracted Doubly Linked list is:
20 12 30 11 36 15Time Complexity To Convert Binary Tree To Doubly Linked List: O(N), as tree traversal is needed.
Space Complexity To Convert Binary Tree To Doubly Linked List: O(N), for the recursion stack and the doubly linked list.
Now, let us have a look at another approach. The time complexities of both the approaches are the same.
Approach#2 To Convert Binary Tree To Doubly Linked List
The approach is going to be pretty simple. We will do the in-order traversal of the given tree, and one by one, change the links of each node that we encounter. The doubly linked list will be created In-Place. Let us have a look at the algorithm to get a clearer look.
Algorithm To Convert Binary Tree To Doubly Linked List
- Base Case – If the root is NULL, return NULL.
- Create a node prev and initialize with NULL.
- Recur for the left subtree.
- Now, if prev is NULL, then the root will be the head of our doubly linked list.
- Else, the left of the root will point to prev and the right of prev will point to the root.
- After the above conditional statements, change the value of prev to root.
- In the end, recur for the right subtree.
Code Implementation To Convert Binary Tree To Doubly Linked List
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct node
{
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
/* This is the core function to convert Tree to list. This function follows
steps 1 and 2 of the above algorithm */
struct node* bintree2listUtil(struct node* root)
{
// Base case
if (root == NULL)
return root;
// Convert the left subtree and link to root
if (root->left != NULL)
{
// Convert the left subtree
struct node* left = bintree2listUtil(root->left);
// Find inorder predecessor. After this loop, left
// will point to the inorder predecessor
for (; left->right!=NULL; left=left->right);
// Make root as next of the predecessor
left->right = root;
// Make predecessor as previous of root
root->left = left;
}
// Convert the right subtree and link to root
if (root->right!=NULL)
{
// Convert the right subtree
struct node* right = bintree2listUtil(root->right);
// Find inorder successor. After this loop, right
// will point to the inorder successor
for (; right->left!=NULL; right = right->left);
// Make root as previous of successor
right->left = root;
// Make successor as next of root
root->right = right;
}
return root;
}
// The main function that first calls bintree2listUtil(), then follows step 3
// of the above algorithm
struct node* bintree2list(struct node *root)
{
// Base case
if (root == NULL)
return root;
// Convert to DLL using bintree2listUtil()
root = bintree2listUtil(root);
// bintree2listUtil() returns root node of the converted
// DLL. We need pointer to the leftmost node which is
// head of the constructed DLL, so move to the leftmost node
while (root->left != NULL)
root = root->left;
return (root);
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* new_node = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
new_node->data = data;
new_node->left = new_node->right = NULL;
return (new_node);
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list */
void printList(struct node *node)
{
while (node!=NULL)
{
printf("%d ", node->data);
node = node->right;
}
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
// Let us create the tree shown in above diagram
struct node *root = newNode(11);
root->left = newNode(12);
root->right = newNode(15);
root->left->left = newNode(20);
root->left->right = newNode(30);
root->right->left = newNode(36);
// Convert to DLL
struct node *head = bintree2list(root);
// Print the converted list
printList(head);
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
};
void BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(node *root, node **head)
{
// Base Case
if (root == NULL) return;
// Create a prev node
static node* prev = NULL;
// Recur for left subtree
BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root->left, head);
// Make the leftmost element the head ofr DLL
if (prev == NULL)
*head = root;
else
{
// Change links
root->left = prev;
prev->right = root;
}
// Change the value of prev to root
prev = root;
BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root->right, head);
}
node* newNode(int data)
{
node* new_node = new node;
new_node->data = data;
new_node->left = new_node->right = NULL;
return (new_node);
}
void printList(node *node)
{
while (node!=NULL)
{
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->right;
}
int main()
{
node *root = newNode(11);
root->left = newNode(12);
root->right = newNode(15);
root->left->left = newNode(20);
root->left->right = newNode(30);
root->right->left = newNode(36);
node *head = NULL;
BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root, &head);
printList(head);
return 0;
}
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
Node head;
static Node prev = null;
void BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
return;
BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root.left);
if (prev == null)
head = root;
else
{
root.left = prev;
prev.right = root;
}
prev = root;
BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root.right);
}
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null)
{
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.right;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(11);
tree.root.left = new Node(12);
tree.root.right = new Node(15);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(20);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(30);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(36);
tree.BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(tree.root);
tree.printList(tree.head);
}
}
Output:
20 12 30 11 36 15Time Complexity To Convert Binary Tree To Doubly Linked List: O(N), as a simple in-order traversal is needed.
Space Complexity To Convert Binary Tree To Doubly Linked List: O(N), the space required for recursion stack.
This blog discusses different approaches to convert binary tree to doubly linked list. This is a very important problem when it comes to coding interviews. Solving daily questions for the topics like linked list will definitely help in conquering your dream, you can follow this link Linked List for practicing more questions of linked list.
FAQ
1. How do you convert a given binary tree to a doubly linked list?
This can be achieved by traversing the tree in the in-order manner, that is, left the child -> root ->right node. Traverse left subtree and convert it into the doubly linked list by adding nodes to the end of the list. In this way, the leftmost node will become head of the list.
2. Is a doubly linked list faster?
Accessing elements in a Doubly Linked List is more efficient when compared to a Singly Linked List as both forward and backward traversal is possible. The time complexity of inserting or deleting a node at a given position (if the pointer to that position is given) in a singly linked list is O(n).
3. Which companies had recently asked the conversion of binary trees into doubly linked lists?
Amazon, Samsung, Indiamart, Flipkart and Zscaler in their recent interviews had asked this question.