CONCEPTS USED:
Sliding Window Technique
DIFFICULTY LEVEL:
Medium
PROBLEM STATEMENT(SIMPLIFIED):
Given an array
A, we need to find two sub-arrays with specific lengthsLandRsuch that sum of these sub-arrays isMaximumamong all possible choices of sub-arrays and these sub-arrays don’t overlap each other.
NOTE:
Both sub-arrays should be continuous and should not contain same element.
Sub-array L can come after or before sub-array R.
For Example:
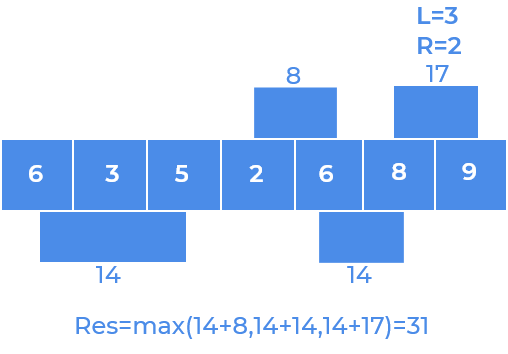
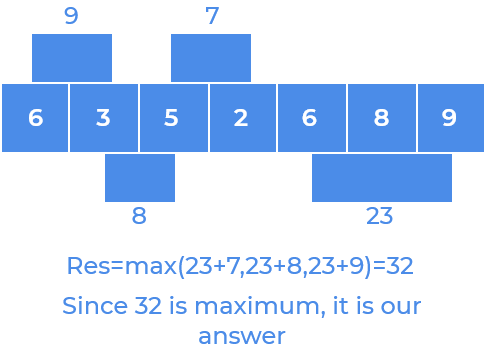
Input : A = [6, 3, 5, 2, 6, 8, 9]
L = 3, R = 2
Output : 32
Explanation: There can be many possible sub-arrays -
[6, 3, 5] [2, 6]
[6, 3, 5] [6, 8]
[6, 3, 5] [8, 9]
[3, 5, 2] [6, 8]
[3, 5, 2] [8, 9]
[5, 2, 6] [6, 3]
[5, 2, 6] [8, 9]
[2, 6, 8] [6, 3]
[2, 6, 8] [3, 5]
[6, 8, 9] [6, 3] --> It gives us maximum value = 32
[6, 8, 9] [3, 5]
[6, 8, 9] [5, 2]SOLVING APPROACH:
BRUTE FORCE METHOD:
The simple solution would be to first traverse a sub-array for
Lelements and look for another sub-array withRelements from the remaining elements in the array ,take out theirSumand compare it with the initial max value.Repeat this process for all such sub-arrays with length
LandRand return the maximum possible value found.
Time Complexityof this solution will beO(N^2).
EXAMPLE:
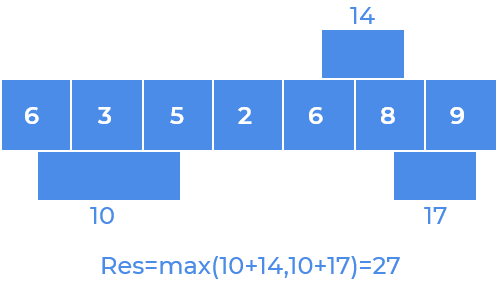
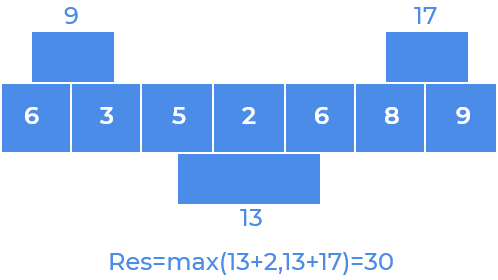
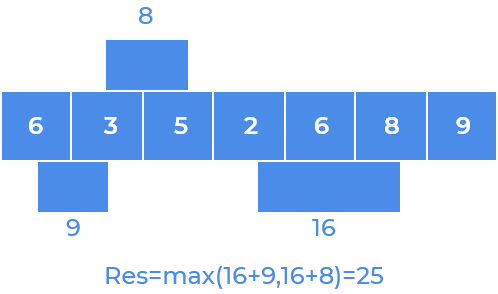
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
EFFICIENT METHOD:
The idea is to use
Sliding Window Technique, where we create a window of(L+R)elements initially and keep processing all such windows present in the array.Assume initialize variables
Resultas sum of first window of size(L+R),lmaxas sum of firstLelements andrmaxas sum of firstRelements.Now move to the next window, we have two cases :
Lcomes beforeR.Rcomes beforeL.When
Lcomes beforeR, we will find the sum of startingLelements of the current window ascurrent leftand compare it with ourlmaxvalue, the higher of the two will be stored inlmax, similarly calculate the sum ofRelements ascurrent right, and compare the currentlmax+current rightwithResultand store the maximum of two in theResult.When
Rcomes beforeL, we will find the sum of startingRelements of the current window ascurrent rightand compare it with ourrmaxvalue, the higher of the two will be stored inrmax, similarly calculate the sum ofLelements ascurrent left, and compare the currentrmax+current leftwithResultand store the maximum of two in theResult.Similarly all such windows are processed from
i= (left+right)toi<N.
NOTE: For finding the sum of ranges of array elements quickly, Prefix Sum Array can be used, which gives us the sum of any range of elements in an array in O(1) Time Complexity.
Illustration of Prefix Sum Array:
A[] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
Prefix[] = [1, 3, 6, 10, 15]
where Prefix[index] gives us the sum of array till i = index.
Prefix[3] = 10
Sum of elements in range [left, right] = Prefix[right] - Prefix[left-1]
sum [2, 4] = Prefix[4] - Prefix[2-1]
= 15 - 3
= 12SOLUTIONS
#include <stdio.h>
int max(int a, int b){
return (a>b) ? a:b;
}
int maxSumTwoNoOverlap(int *arr, int n, int l, int r){
/* creating prefix sum array from existing array */
for(int i=1; i<n; i++)
arr[i] += arr[i-1];
//initialize current values
int res = arr[l+r-1];
int lmax = arr[l-1];
int rmax = arr[r-1];
/* Running loop for traversing all the windows and
taking max values of left right and result */
for(int i = l+r; i<n; i++){
lmax = max(lmax, arr[i-r] - arr[i-r-l]);
res = max(res, arr[i] - arr[i-r] + lmax);
rmax = max(rmax, arr[i-l] - arr[i-r-l]);
res = max(res, arr[i] - arr[i-l] + rmax);
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
int t; scanf("%d", &t);
while(t--){
int n; scanf("%d", &n);
int arr[n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
scanf("%d", &arr[i]);
int l, r; scanf("%d %d", &l , &r);
printf("%d\n", maxSumTwoNoOverlap(arr, n, l, r));
}
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int maxSumTwoNoOverlap(int *arr, int n, int l, int r){
/* creating prefix sum array from existing array */
for(int i=1; i<n; i++)
arr[i] += arr[i-1];
//initialize current values
int res = arr[l+r-1];
int lmax = arr[l-1];
int rmax = arr[r-1];
/* Running loop for traversing all the windows and
taking max values of left right and result */
for(int i = l+r; i<n; i++){
lmax = max(lmax, arr[i-r] - arr[i-r-l]);
res = max(res, arr[i] - arr[i-r] + lmax);
rmax = max(rmax, arr[i-l] - arr[i-r-l]);
res = max(res, arr[i] - arr[i-l] + rmax);
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
int t; cin>>t;
while(t--){
int n; cin>>n;
int arr[n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
cin>>arr[i];
int l, r; cin>>l>>r;
cout<<maxSumTwoNoOverlap(arr, n, l, r)<<"\n";
}
return 0;
}
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.Math;
public class Main {
static int maxSumTwoNoOverlap(int []arr, int n, int l, int r){
/* creating prefix sum array from existing array */
for(int i=1; i<n; i++)
arr[i] += arr[i-1];
//initialize current values
int res = arr[l+r-1];
int lmax = arr[l-1];
int rmax = arr[r-1];
/* Running loop for traversing all the windows and
taking max values of left right and result */
for(int i = l+r; i<n; i++){
lmax = Math.max(lmax, arr[i-r] - arr[i-r-l]);
res = Math.max(res, arr[i] - arr[i-r] + lmax);
rmax = Math.max(rmax, arr[i-l] - arr[i-r-l]);
res = Math.max(res, arr[i] - arr[i-l] + rmax);
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int t = sc.nextInt();
while(t != 0){
int n = sc.nextInt();
int arr[] = new int[n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
int l = sc.nextInt();
int r = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(maxSumTwoNoOverlap(arr, n, l, r));
t--;
}
}
}
[forminator_quiz id="285"]
This article tried to discuss Sliding Window Technique. Hope this blog helps you understand and solve the problem. To practice more problems on Sliding Window Technique you can check out .