Concepts Used
Breadth First Search
Difficulty Level
Hard
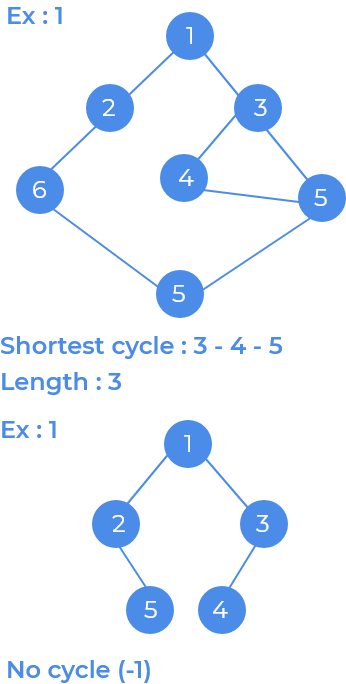
Problem Statement :
Given a graph we have to find the length of the shortest cycle in the given graph. If no cycle exists print
−1.
Solution Approach :
Introduction :
Idea is to check the length of the cycle from every vertex and print the minimum length, if no cycle is present print
-1.We can use BFS to store the cycle length for every vertex.
Description :
We will iterate for all vertices and store distance and parent of every vertex v using distance[ ] and parent[ ] array. Now for every v iterate for all its adjacent vertices a, if a is not visited update its distance (distance[a] = distance[v]+1) and parent (parent[a] = v). If a is already visited check if parent[a] is v or not, if not then there is a cycle. Now update the minimum cycle length if the current cycle length is shorter.
Algorithms :
shortest_cycle() :
-
create a queue and push the current vertex now perform following operations untill the queue is not empty:
-
each time we pop a vertex
vfrom queue, (v= queue.front() ), we will mark the vertexvas visited (visited[v]= true). -
Iterate for all the adjacent vertices of
vand for every adjacent vertexa, do following :- update the parent and distance as,
parent[a] = vanddistance[a]= distance[v]+1. - push
ainto the queue. - if
ais not visited,
and ifparent[v] != a. - update the ans ( ans = min(ans,current cycle length) ).
- update the parent and distance as,
Complexity Analysis:
The time complexity of the above method is represented in the form of
O(V+E), whereVis the number of verices andEis the number of edges.
Solutions:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#define INT_MAX 99999
#define INT_MIN -99999
//ADJACENCY LIST
struct node {
int vertex;
struct node* next;
};
struct node* createNode(int);
struct Graph {
int numVertices;
struct node** adjLists;
};
// Create a node
struct node* createNode(int v) {
struct node* newNode = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newNode->vertex = v;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
// Create a graph
struct Graph* createAGraph(int vertices) {
struct Graph* graph = malloc(sizeof(struct Graph));
graph->numVertices = vertices;
graph->adjLists = malloc(vertices * sizeof(struct node*));
int i;
for (i = 0; i < vertices; i++)
graph->adjLists[i] = NULL;
return graph;
}
// Add edge
void addEdge(struct Graph* graph, int s, int d) {
// Add edge from s to d
struct node* newNode = createNode(d);
newNode->next = graph->adjLists[s];
graph->adjLists[s] = newNode;
// Add edge from d to s
newNode = createNode(s);
newNode->next = graph->adjLists[d];
graph->adjLists[d] = newNode;
}
// Print the graph
void printGraph(struct Graph* graph) {
int v;
for (v = 0; v < graph->numVertices; v++)
{
struct node* temp = graph->adjLists[v];
//printf("\n Vertex %d\n: ", v);
while (temp) {
printf("%d ", temp->vertex);
temp = temp->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
//QUEUE
struct Queue
{
int front, rear, size;
unsigned capacity;
int* array;
};
// function to create a queue of given capacity.
// It initializes size of queue as 0
struct Queue* createQueue(unsigned capacity)
{
struct Queue* queue = (struct Queue*) malloc(sizeof(struct Queue));
queue->capacity = capacity;
queue->front = queue->size = 0;
queue->rear = capacity - 1; // This is important, see the enqueue
queue->array = (int*) malloc(queue->capacity * sizeof(int));
return queue;
}
// Queue is full when size becomes equal to the capacity
int isFull(struct Queue* queue)
{ return (queue->size == queue->capacity); }
// Queue is empty when size is 0
int isEmpty(struct Queue* queue)
{ return (queue->size == 0); }
// Function to add an item to the queue.
// It changes rear and size
void enqueue(struct Queue* queue, int item)
{
if (isFull(queue))
return;
queue->rear = (queue->rear + 1)%queue->capacity;
queue->array[queue->rear] = item;
queue->size = queue->size + 1;
}
// Function to remove an item from queue.
// It changes front and size
int dequeue(struct Queue* queue)
{
if (isEmpty(queue))
return INT_MIN;
int item = queue->array[queue->front];
queue->front = (queue->front + 1)%queue->capacity;
queue->size = queue->size - 1;
return item;
}
// Function to get front of queue
int front(struct Queue* queue)
{
if (isEmpty(queue))
return INT_MIN;
return queue->array[queue->front];
}
int min(int a,int b)
{
return (a<b)?a:b;
}
int shortest_cycle(struct Graph* graph,int n)
{
// To store length of the shortest cycle
int ans = INT_MAX;
// For all vertices
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Make distance maximum
int dist[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
dist[i]=INT_MAX;
// Take a imaginary parent
int par[n] ;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
par[i]= -1;
// Distance of source to source is 0
dist[i] = 0;
struct Queue* q = createQueue(1000);
// Push the source element
enqueue(q,i);
// Continue until queue is not empty
while (!isEmpty(q)) {
// Take the first element
int x = front(q);
dequeue(q);
// Traverse for all it's childs
struct node* temp = graph->adjLists[x];
while(temp) {
// If it is not visited yet
if (dist[temp->vertex] == INT_MAX) {
// Increase distance by 1
dist[temp->vertex] = 1 + dist[x];
// Change parent
par[temp->vertex] = x;
// Push into the queue
enqueue(q,temp->vertex);
}
// If it is already visited
else if (par[x] != temp->vertex)
ans = min(ans, dist[x] + dist[temp->vertex] + 1);
temp = temp->next;
}
}
}
// If graph contains no cycle
if (ans == INT_MAX)
return -1;
// If graph contains cycle
else
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
int n ,e;
scanf("%d %d",&n,&e);
struct Graph* graph = createAGraph(n);
while(e--)
{
int u,v;
scanf("%d %d",&u,&v);
addEdge(graph, u,v);
}
printf("%d\n",shortest_cycle(graph,n));
}
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 10000
vector<int> gr[N];
// Function to add edge
void Add_edge(int x, int y)
{
gr[x].push_back(y);
gr[y].push_back(x);
}
// Function to find the length of
// the shortest cycle in the graph
int shortest_cycle(int n)
{
// To store length of the shortest cycle
int ans = INT_MAX;
// For all vertices
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Make distance maximum
vector<int> dist(n, INT_MAX);
// Take a imaginary parent
vector<int> par(n, -1);
// Distance of source to source is 0
dist[i] = 0;
queue<int> q;
// Push the source element
q.push(i);
// Continue until queue is not empty
while (!q.empty()) {
// Take the first element
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
// Traverse for all it's childs
for (int child : gr[x]) {
// If it is not visited yet
if (dist[child] == INT_MAX) {
// Increase distance by 1
dist[child] = 1 + dist[x];
// Change parent
par[child] = x;
// Push into the queue
q.push(child);
}
// If it is already visited
else if (par[x] != child)
ans = min(ans, dist[x] + dist[child] + 1);
}
}
}
// If graph contains no cycle
if (ans == INT_MAX)
return -1;
// If graph contains cycle
else
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
int n ,e;
cin>>n>>e;
for(int i=0;i<e;i++)
gr[i].clear();
while(e--)
{
int u,v;
cin>>u>>v;
Add_edge(u,v);
}
cout <<shortest_cycle(n)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
static final int N = 100200;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static Vector<Integer>[] gr = new Vector[N];
// Function to add edge
static void Add_edge(int x, int y)
{
gr[x].add(y);
gr[y].add(x);
}
// Function to find the length of
// the shortest cycle in the graph
static int shortest_cycle(int n)
{
// To store length of the shortest cycle
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// For all vertices
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Make distance maximum
int[] dist = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(dist, (int) 1e9);
// Take a imaginary parent
int[] par = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(par, -1);
// Distance of source to source is 0
dist[i] = 0;
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
// Push the source element
q.add(i);
// Continue until queue is not empty
while (!q.isEmpty())
{
// Take the first element
int x = q.poll();
// Traverse for all it's childs
for (int child : gr[x])
{
// If it is not visited yet
if (dist[child] == (int) (1e9))
{
// Increase distance by 1
dist[child] = 1 + dist[x];
// Change parent
par[child] = x;
// Push into the queue
q.add(child);
}
else if (par[x] != child && par[child] != x)
ans = Math.min(ans, dist[x] + dis[child] + 1);
}
}
}
// If graph contains no cycle
if (ans == Integer.MAX_VALUE)
return -1;
// If graph contains cycle
else
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int t = sc.nextInt();
while(t-->0)
{
int n = sc.nextInt();
int e = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
gr[i] = new Vector<>();
while(e-->0)
{
int u = sc.nextInt();
int v = sc.nextInt();
Add_edge(u,v);
}
// Function call
System.out.println(shortest_cycle(n));
}
}
}
[forminator_quiz id="2125"]
This article tried to discuss Breadth First Search. Hope this blog helps you understand and solve the problem. To practice more problems on Breadth First Search you can check out .