Concepts Used
Breadth First Search
Difficulty Level
Medium
Problem Statement :
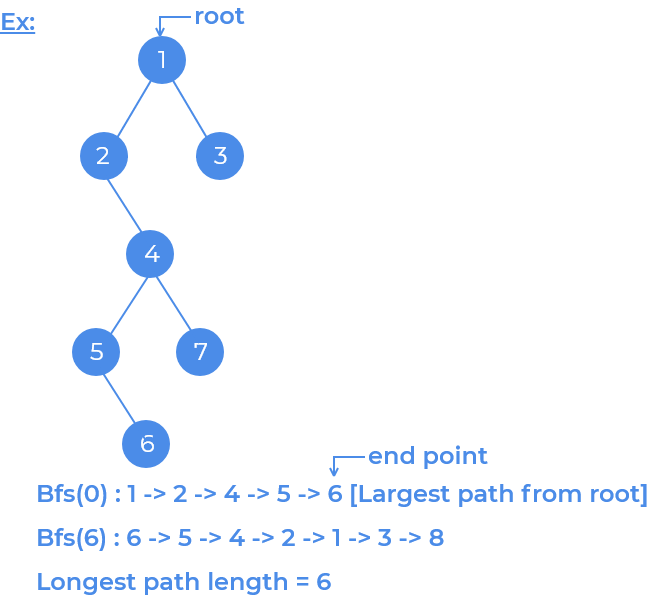
Given an unweighted, undirected tree print the length of the longest path
Solution Approach :
Introduction :
Path lenght is the number of edges from one vertex (source) to another (destination). Idea is to perform bfs and store the distance of every vertex, print maximum among all the distances.
Description :
We are going to perform two bfs in order to find maximum path length. One for storing the path length from any of the vextex (source) ,lets say vertex
v. We will see how far we can go from this vertexv. Another bfs to count the actual path length. This time our source vertex will bevand we will move as far as possible, while maintaining adistance[]array to store the distances for every vertex and finally return the maximum among all the distances.
Algorithms :
bfs() :
- create a queue and push the current vertex
vand update the distance ofv(distance[v]=0). (vis the source vertex), now perform following operations untill the queue is not empty:- each time we pop a vertex
vfrom queue, (v= queue.front() )- Iterate for all the adjacent vertices of
vand for every adjacent vertexa, do following :
- if
ais unvisited update the distance as,distance[a]= distance[v]+1. - push
ainto the queue.
- Now when the queue becomes empty, iterate for all the vertices and return the maximum distance.
Complexity Analysis:
As we are performing two simple bfs, the time complexity of the this method is represented in the form of
O(V+E), whereVis the number of verices andEis the number of edges.
Solutions:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#define INT_MIN -9999
struct pair {
void *first;
void *second;
};
void FreePair(struct pair* pair) {
free(pair->first);
free(pair->second);
free(pair);
}
struct pair* MakePair(void *f, void *s, size_t fsize, size_t ssize) {
struct pair* p = malloc(sizeof(struct pair));
if (p == NULL) return NULL;
p->first = malloc(fsize);
p->second = malloc(ssize);
if (p->first == NULL || p->second == NULL) {
FreePair(p);
return NULL;
}
memcpy(p->first, f, fsize);
memcpy(p->second, s, ssize);
return p;
}
//ADJACENCY LIST
struct node {
int vertex;
struct node* next;
};
struct node* createNode(int);
struct Graph {
int numVertices;
struct node** adjLists;
};
// Create a node
struct node* createNode(int v) {
struct node* newNode = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newNode->vertex = v;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
// Create a graph
struct Graph* createAGraph(int vertices) {
struct Graph* graph = malloc(sizeof(struct Graph));
graph->numVertices = vertices;
graph->adjLists = malloc(vertices * sizeof(struct node*));
int i;
for (i = 0; i < vertices; i++)
graph->adjLists[i] = NULL;
return graph;
}
// Add edge
void addEdge(struct Graph* graph, int s, int d) {
// Add edge from s to d
struct node* newNode = createNode(d);
newNode->next = graph->adjLists[s];
graph->adjLists[s] = newNode;
// Add edge from d to s
newNode = createNode(s);
newNode->next = graph->adjLists[d];
graph->adjLists[d] = newNode;
}
//QUEUE
struct Queue
{
int front, rear, size;
unsigned capacity;
int* array;
};
// function to create a queue of given capacity.
// It initializes size of queue as 0
struct Queue* createQueue(unsigned capacity)
{
struct Queue* queue = (struct Queue*) malloc(sizeof(struct Queue));
queue->capacity = capacity;
queue->front = queue->size = 0;
queue->rear = capacity - 1; // This is important, see the enqueue
queue->array = (int*) malloc(queue->capacity * sizeof(int));
return queue;
}
// Queue is empty when size is 0
int isEmpty(struct Queue* queue)
{ return (queue->size == 0); }
// Function to add an item to the queue.
// It changes rear and size
void enqueue(struct Queue* queue, int item)
{
queue->rear = (queue->rear + 1)%queue->capacity;
queue->array[queue->rear] = item;
queue->size = queue->size + 1;
//printf("%d enqueued to queue\n", item);
}
// Function to remove an item from queue.
// It changes front and size
int dequeue(struct Queue* queue)
{
if (isEmpty(queue))
return INT_MIN;
int item = queue->array[queue->front];
queue->front = (queue->front + 1)%queue->capacity;
queue->size = queue->size - 1;
return item;
}
// Function to get front of queue
int front(struct Queue* queue)
{
if (isEmpty(queue))
return INT_MIN;
return queue->array[queue->front];
}
struct pair* bfs(struct Graph *graph, int u,int V)
{
int dis[V];
memset(dis, -1, sizeof(dis));
struct Queue* q = createQueue(100000);
enqueue(q,u);
dis[u] = 0;
while (!isEmpty(q))
{
int t = dequeue(q);
struct node * temp = graph->adjLists[t];
while(temp)
{
if (dis[temp->vertex] == -1)
{
enqueue(q,temp->vertex);
dis[temp->vertex] = dis[t] + 1;
}
temp = temp->next;
}
}
int maxDis = 0;
int nodeIdx;
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
if (dis[i] > maxDis)
{
maxDis = dis[i];
nodeIdx = i;
}
}
return MakePair(&nodeIdx, &maxDis,sizeof(nodeIdx),sizeof(maxDis));
}
void longestPathLength(struct Graph* graph,int n)
{
struct pair * t1,*t2;
t1 = bfs(graph,0,n);
t2 = bfs(graph,*(int *)t1->first,n);
printf("%d\n", *(int *)t2->second);
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
int n,m,u,v;
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
struct Graph* graph = createAGraph(n);
while(m-->0)
{
int a,b;
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
addEdge(graph,a,b);
}
longestPathLength(graph,n);
}
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Graph
{
int V;
list<int> *adj;
public:
Graph(int V);
void addEdge(int v, int w);
void longestPathLength();
pair<int, int> bfs(int u);
};
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list<int>[V];
}
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].push_back(w);
adj[w].push_back(v);
}
pair<int, int> Graph::bfs(int u)
{
int dis[V];
memset(dis, -1, sizeof(dis));
queue<int> q;
q.push(u);
dis[u] = 0;
while (!q.empty())
{
int t = q.front(); q.pop();
for (auto it = adj[t].begin(); it != adj[t].end(); it++)
{
int v = *it;
if (dis[v] == -1)
{
q.push(v);
dis[v] = dis[t] + 1;
}
}
}
int maxDis = 0;
int nodeIdx;
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
if (dis[i] > maxDis)
{
maxDis = dis[i];
nodeIdx = i;
}
}
return make_pair(nodeIdx, maxDis);
}
void Graph::longestPathLength()
{
pair<int, int> t1, t2;
t1 = bfs(0);
t2 = bfs(t1.first);
cout<< t2.second<<endl;
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
int n,e;
cin>>n>>e;
Graph g(n);
while(e--)
{
int u,v;
cin>>u>>v;
g.addEdge(u,v);
}
g.longestPathLength();
}
return 0;
}
import java.util.*;
class Main {
static class Pair<T,V> {
T first;
V second;
Pair(T first, V second) {
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
static class Graph {
int V;
LinkedList<Integer>[] adj;
// Constructor
Graph(int V) {
this.V = V;
adj = new LinkedList[V];
for(int i = 0; i < V; ++i) {
adj[i] = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
}
void addEdge(int s, int d) {
adj[s].add(d);
adj[d].add(s);
}
Pair<Integer, Integer> bfs(int u) {
int[] dis = new int[V];
Arrays.fill(dis, -1);
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(u);
dis[u] = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int t = q.poll();
for(int i = 0; i < adj[t].size(); ++i) {
int v = adj[t].get(i);
if(dis[v] == -1) {
q.add(v);
dis[v] = dis[t] + 1;
}
}
}
int maxDis = 0;
int nodeIdx = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < V; ++i) {
if(dis[i] > maxDis) {
maxDis = dis[i];
nodeIdx = i;
}
}
return new Pair<Integer, Integer>(nodeIdx, maxDis);
}
void longestPathLength() {
Pair<Integer, Integer> t1, t2;
t1 = bfs(0); // first bfs
// second bfs to find actual longest path
t2 = bfs(t1.first);
System.out.println(t2.second);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
// Create a graph given in the example
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int t = sc.nextInt();
while(t-->0)
{
int n = sc.nextInt();
int e = sc.nextInt();
Graph graph = new Graph(n);
while(e-->0)
{
int u = sc.nextInt();
int v = sc.nextInt();
graph.addEdge(u,v);
}
graph.longestPathLength();
}
}
}
[forminator_quiz id="1941"]
This article tried to discuss Breadth First Search. Hope this blog helps you understand and solve the problem. To practice more problems on Breadth First Search you can check out .